Social Innovation - the What, Why and How
When thinking of innovation, we usually think of new technologies developed by companies as engines for their own growth. However, there is more than that to innovation. It doesn’t just help companies grow; it also helps the society prosper. Today we’ll dive deeper into social innovation and show how it can serve your business.

Table of contents
What is social innovation?
Social innovation refers to the process of developing and implementing new, effective solutions to solve social or environmental issues. Whether these come from national policies, governmental or non-governmental entities, such solutions should meet current social needs better than it has been done before.
Social innovation is meant to have long term impact at large scale. Social innovation is traditionally advanced through non-profit endeavours, but the business community is also open to address society’s challenges too.
Why social innovation is important
In today’s hyperconnected world, one country’s societal problems can become ours. Nations are facing slow economic growth, financial instability, political turmoil, hunger, poverty and disease. These are all social issues that have to be addressed, one way or the other, and such big problems generate big business opportunities. In fact, more than 80% of economic growth comes from innovation and application of new knowledge.
A truly prosperous society in our days consists of both economic prosperity and social prosperity. Traditionally, we assessed if a country was prosperous by looking at its GDP. Today, it’s becoming more common to also consider peace and happiness, individual freedoms and liberties and financial wellbeing.
When we look at prosperity from this angle, we see that prosperous societies have an innovative approach to current social issues because our complex problems need new solutions. Social innovation brings a new mindset that leaves behind the narrow way of thinking about social enterprises and for-profit businesses as two mutually exclusive areas.
Social innovation is mistakenly seen by some as charity. It should be acknowledged that social innovation is actually adding an extra dimension to innovation, sustaining economic and social growth.
Embracing social innovation is not just about doing good for the society but also about doing good business. Let’s see why we should question the utility of traditional corporate philanthropy and instead take a closer look at the business value of social innovation.
The difference between Corporate Social Innovation and Corporate Social Responsibility
Since we are talking about social innovation from a business perspective, we should clarify the difference between the terms used to refer to environmental and social responsibility in the corporate world.- Let’s start with our topic of interest in this article: corporate social innovation (CSI). CSI refers to companies that integrate social innovation in their business activities. This can be seen as an ongoing approach that seeks to continuously address social challenges and improve on these solutions.
- On the other hand, there is also the Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) approach which has become quite common for companies. CSR refers to strategies that ensure a company’s operations are ethical and beneficial to society. CSR generally covers four main areas: philanthropy, environment, human rights and economic responsibility.
It has been argued that CSR is an old habit in need for an upgrade. If we look at the philanthropic area of CSR, it might be true. It seems that companies started shifting towards social innovation and stopped calling their strategic approach to social responsibility CSR.
In this article we are making the case of why social innovation is a more powerful and valuable approach to CSR, both for business and for society. Because social innovation is actually trying to solve problems to their roots, companies should acknowledge the business opportunity in creating solutions for these problems.
 To explain this better, we could draw a parallel with the role of continuous improvement. It enables companies to become better and support innovation. We touched here on the topic of how important it is to get down to the root of a problem when you want to improve something. Philanthropy, however, does not really go to the root of the problem. So, it is often not actually improving anything, it is merely alleviating the symptoms of a bigger issue.
To explain this better, we could draw a parallel with the role of continuous improvement. It enables companies to become better and support innovation. We touched here on the topic of how important it is to get down to the root of a problem when you want to improve something. Philanthropy, however, does not really go to the root of the problem. So, it is often not actually improving anything, it is merely alleviating the symptoms of a bigger issue.
SI & the business opportunity of social and environmental megatrends
So, what are some of the megatrends that could generate corporate social innovation? How are companies getting the business benefits in following the trends of the future?
Urbanization
There are 80 million forcibly displaced people worldwide and as numbers continue to increase urban areas have to deal with new challenges. There’s an increasing need to tackle diversity in a more innovative way, to organize schools, language training and housing to fit the current population.

Smart cities are no longer technology-centric, but citizen-centric. Studies show that more inclusive cities have better economic health. Social innovation can bring greater value to public services by catering more effectively and holistically to the needs of populations.
Social innovation can bring greater value to public services by catering more effectively and holistically to the needs of populations.
CHAOS Architects is a Finnish company harnessing the power of data, technology and people to enable sustainable urban development. Their smart city platform combines urban data with human perspective to support both public institutions and private companies in developing cities that answer to current needs and challenges.
Their innovative solution benefits society: they help make liveable cities by putting the residents at the core. At the same time, they focus on the economic value: they use data as a solution to support better decision making in real estate investment and development.
For example, one of their customers operating in the construction sector uses their platform to get insights on optimal locations for different property types based on diversity, mobility, accessibility.
Health and wellness
Healthcare systems around the world were under great pressure even before the global pandemic. They are facing the challenge of an ageing population whose issues are overloading the healthcare system and at the same time an increase in chronic diseases puts an extra strain on healthcare costs.
In the US, chronic disease affects 50% of the population and its care amounts to more than 85% of health care costs. Preventing or managing symptoms where possible, can dramatically reduce costs.
In the preventive approach of fighting such diseases we should also take into account behavioural problems like addictions and obesity. Just to name an example here, we could have a look at Virta health, an innovative company tackling the problem of diabetes. Their solution is addressing the root cause of the issue through continuous remote medical care and individualized nutrition therapy.
The mismatch between growing GDP and stagnating happiness
What makes people happy, content and fulfilled and how are these linked with innovation? Drawing on recent research we can argue that there is a connection between social well-being and innovation.
For the fourth time in a row, the World Happiness Report found Finland to be the happiest country in the world. It is closely followed by countries like Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland and Netherlands. What do these countries have in common? They are prosperous societies that provide social well-being and also rank in the top ten of the most innovative countries worldwide.
We can conclude that a growing GDP is not enough to create happy, prosperous societies, as they need more than just financial power. China is the country with the second highest GDP, but it’s far from having a prosperous society in the broader sense.
The economics of happiness is not a new concept, but more companies start seeing its business value, especially when they tap into the role of wellness and wellbeing in productivity growth. Companies like Calm that provides an app for meditation and sleep made its business and primary goal to make the world happier. While there are many similar products on the market, Calm was the first to reach a valuation worth of $1 billion.
Climate change
Climate change is getting all the attention for some years and for good reason. It’s also the area that sees most innovation as cities, transport, and housing have to be dramatically reorganized to reduce carbon emissions and adapt to climate change.

There are various social innovators that work on solutions for climate change: from the more famous ones like electric cars, to those trying to educate and increase awareness with carbon calculators or alternative protein sources like Beyond Meat.
Best practices for good corporate social innovation
Now that we had a look at the megatrends and needs in social innovation, let’s see some of the principles that contribute to the success of corporate social innovation.
1. Strategic intent
Corporate social innovation has to be embedded in the core business strategy and should consider the organization’s vision. For this, top management support and accountability are mandatory.
For example, Unilever integrated CSI in their core business through the Unilever Sustainable Living Plan. They committed to growing their company while tackling environmental issues and social inequalities. To do so, they integrated CSI in all their business operations: product design, marketing, sourcing, customer engagement etc.
Their ambition to grow is supported by innovation and their strategy includes goals like reducing their environmental impact by half by 2030 and improve health and wellbeing for 1 billion people.
2. Leverage the power of different markets
Through corporate innovation companies can identify new, underserved markets to expand to. These can be either within local markets or in emerging economies. By leveraging these markets, organizations can serve unmet needs with new products or services.
In our interview with John Carter on innovation beyond the core, we talked about what made some big companies like Amazon and Apple so successful. His finding in working with these companies was that they innovate not only in their core product areas, but also outside of that core business.
 Just think of the business opportunities that can rise from going into markets where the public sector or charitable organizations have been the main actors for a long time. You don’t have to struggle for market share in areas where competition might be fierce when you can identify areas where problems have not been addressed at the root.
Just think of the business opportunities that can rise from going into markets where the public sector or charitable organizations have been the main actors for a long time. You don’t have to struggle for market share in areas where competition might be fierce when you can identify areas where problems have not been addressed at the root.
You don’t have to struggle for market share in areas where competition might be fierce when you can identify areas where problems have not been addressed at the root.
An example in this case is Grameen Danone, a joint venture and a social business success that identified a new consumer segment in Bangladesh. In an area where 56% of preschool children suffer from malnutrition, Grameen Danone effectively reached a new market in a meaningful way.
The model they developed with Grameen in Bangladesh and Lemateki in Senegal is seen as true disruptive innovation. They developed and industrialized new products to fit the needs of a different market, like fortified yoghurt for local populations and the carton pouch (Shokti Pocket) made of local grains, that can be stored at room temperature. As an efficient model of capital development, they introduced micro-factories and used renewable energies.
The Grameen Danone case serves as a good example of the possibilities that are available in a seemingly unattractive, low-income market.
3. Strategic collaborations
Many companies that succeed at innovation have involved external stakeholders in their innovation process. In fact, 54% of businesses say that co-creation has helped improve their social impact.
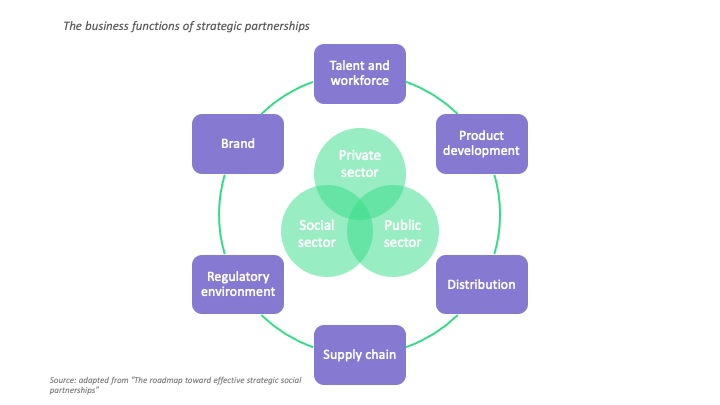
Deloitte researched the opportunities and challenges brought by strategic social partnerships. For effective collaborations in innovation initiatives, consider these five factors that successful partnerships usually meet:
- Include non-profits, social and public organizations
- Back up your mission financially
- Clearly define the business goals that are led by a business unit and not CSR departments
- Set a clear strategy to include impact measurement procedures, rules around communication as well as an exit strategy
- Consider specific goals and challenges that the collaboration can solve
As an example, let’s consider the partnership between Walmart and Care International that was set to provide leadership development and life skills training to more than 60,000 women who work in factories that supply to Walmart. Beyond the social value, they are also looking at their business interest: retain and promote talent within the factories.
Google is also using the power of innovative partnerships to help refine products like Google Earth and Google Maps. They teamed up with local NGOs, universities and World Bank to support their goals (track environmental degradation, spread of viruses, community mappings etc.) which in return gives Google more accurate information that improves their services.
What are the benefits of corporate social innovation
Historically, companies were closely linked to communities. As they got bigger and reached global communities, their role in society faded. Some companies couldn’t find a financially viable model to support their growth, so their priorities had to change. Now times are changing, and corporations are again starting to see the true benefits of CSI.
For social innovation to work well, it has to be tied to business objectives that bring financial value. This means that there is incentive to continuously improve and grow these efforts. In return, on the long term, the business benefits are also increasing.
So, what benefits can you leverage in practice?
1. Workforce competitiveness
CSI can work as a powerful tool to attract, engage and retain great talent. As younger generations seek careers with purpose, companies have to adapt.
In a recent McKinsey research about the role of purpose in organizations, 70% of employees said that their sense of purpose is defined by their work. Employees who have a sense of purpose at work are more dedicated and more capable to innovate.
Talent is one of those resources that fuel innovation, so companies are competing at attracting the best people to their teams. Tesla is famously attracting the best talent and their position as the most attractive employer is giving them an advantage on the market.
2. Business growth
Addressing social and environmental issues is not just good for the society, but also for business. As we mentioned earlier, the business growth opportunity comes especially in addressing new markets that need innovative solutions.
Companies usually have to tackle the issues in these areas by adapting their services and products, while considering the infrastructure and low-purchase power in the region. Even though challenging, these environments also create the possibility for micro-entrepreneurship which can also enhance incomes.
Allianz expanded its geographic reach by first offering insurance products in India to a new customer segment that had lower income. Soon after, Allianz subsidiaries expanded in South America and other countries in Asia and Africa, so they created the Emerging Consumers business units to serve these markets.
While smaller than its traditional business, they still managed to create a profitable micro-insurance business for 11 new markets where they insure 57.4 million people.
3. Strengthen the supply chain
By innovating in their supply chain, companies can get both social and financial gains. The World Economic Forum report is emphasizing the key benefits of social innovation in the corporate supply chain: ensuring robust and sustainable access to raw materials and enhanced reputation by actively responding to consumer needs.
Confectionary company Ferrero invested in Georgia as a means to establish a new source of supply chain and increase incomes and quality standards for the small suppliers they had in the country. They established a strategic partnership with USAID and AgriGeorgia to create a scalable and stable hazelnut supply chain.
Through the partnerships they developed they delivered training programs on modern hazelnut production practices and established groups to improve smallholder farmers access to finance. As a result, more than 2,100 hazelnut farmers have increased their quantity and quality of their production and Ferrero established a new sustainable source of raw materials for its products.
4. Brand value
Globalization has brought its share of good and bad to the world and to corporations. Greater transparency can be seen from two angles, as it makes companies more accountable for their actions but also more vulnerable to public opinion.
Customers expect more from their service or product providers. As cancel culture is gaining more traction, companies have started to realize how powerful consumers can be when something goes against their own values and beliefs. Companies can either take advantage and stand out or fall prey by not aligning their values with the current social needs.
How to get started with social innovation
Historically, for-profit organizations were after one main goal: profit. This is deeply embedded in most of their DNA and balancing both social and financial goals doesn’t come natural to them.

So how to approach social innovation while sustaining the company’s growth?
To help you get started and give you a boost of confidence and inspiration, these four steps can give a solid start for your social innovation initiative.
1. Get everyone involved
Social innovation cannot be done overnight. It takes time and commitment, just like any other kind of innovation. You have to remember, and to remind all those involved, that social innovation is a business case in itself and getting everyone talking and excited is just the first step.Get everyone involved through an idea challenge and gather ideas that will fuel your innovation strategy. This could also support your cause and further convince management to get it rolling.
2. Build partnerships
Many companies that do well with social innovation have strong partnerships that help them achieve specific goals. Building strong social partnerships should be a two-way street. A company has a lot to offer in terms of resources, geographic reach, human capital, infrastructure, but it can also have a lot to gain.
We already mentioned some successful partnerships set up by Google, Ferrero or Walmart, but not everyone will succeed. There are many challenges to take into account when trying to team up with other organizations. Misalignment of social impact programs and corporate strategies can lead to wasted resources and failed partnerships. Establishing clear roles and responsibilities for each partner involved can also be challenging.
3. Re-evaluate how you measure success
For your social metrics you should also start looking into outcomes and impact. Start by setting simple KPIs and make sure you measure social performance along with business performance.
How could your KPIs better represent the interconnectivity between the inputs and the impact? For example, use a scorecard that brings together current initiatives, track their performance and create a feedback loop to ensure continuous improvement.
As part of their Health for Humanity Strategy, Johnson & Johnson is focusing on Sustainable Development Goals. They are committed to evaluate and continuously improve their products using a scorecard with seven major goals, among which environmental impact, positive social impact and product innovation.
For example, they want to achieve their environmental impact goal by reducing their carbon emissions 20% by 2020 and 80% by 2050. In terms of energy consumption, they aim to produce or procure 35% of their electricity from renewable sources by 2050. As of 2020 they say they got to 30% of their goal.
4. Enable a culture of innovation
Fostering an innovation culture should be a given in any company, but it’s more often than not the first barrier for innovation performance. Building an environment that encourages and enables innovation takes time and effort.
 It’s good to keep in mind that even though a change in the corporate culture starts with the leaders, it is also enforced from the bottom-up. Management has to take on the responsibilities of communicating, allocating resources and getting the right people on board.
It’s good to keep in mind that even though a change in the corporate culture starts with the leaders, it is also enforced from the bottom-up. Management has to take on the responsibilities of communicating, allocating resources and getting the right people on board.
Some of the simple steps that can help create a more innovative culture: start an idea challenge to ask for employees’ input, feedback and improvement suggestions. Reward and celebrate employees who contribute to new innovations and give anyone the chance to test their ideas.
We wrote an extensive article on this topic that guides you in creating a more innovative culture.
The challenges of social innovation
Many businesses fail to achieve innovation that brings both social and business benefits. Why is that and how can you overcome these challenges?
Demand for growth
Shareholders often put pressure on businesses to get short term profit and this is underserving the vision.

Short term profitability and long-term sustainability are often opposing forces so leaders should do a good job at explaining this. Innovation sometimes fails because businesses focus on monthly, quarterly or annual financial objectives at the expense of long-term perspectives.
Leaders face the big challenge of doing good business with social innovations, otherwise their company’s future is at stake. They should put a lot of effort into orchestrating a transition plan that will allow them to integrate social innovation into their business strategy.
Scepticism
Internally, companies are suspected of not pursuing real business activities. Externally, they are seen as pursuing just financial goals and not really trying to have a social impact.
Considering that many social innovations target unfamiliar segments of customers or markets, the already established internal structures in companies are wary of changing things that work. Leaders also play an important role as they can support innovators to win over the sceptics and gain legitimacy for the efforts.
One way to go around the challenge of internal mistrust is to establish incubators, like Philips did to test their new ideas before they proved viable and scalable. Leaders were also onboard to support their social mission through public commitment and ongoing help.
External scepticism can come from different sides and it can also make it harder to build partnerships. Companies have to win the trust of public stakeholders by reinforcing their social motives, showing they are willing to make real investment and going public about their efforts.
Examples of great Social Innovations
Let’s see some of the most interesting and important cases where companies have done social innovation well. There are also great examples you can learn from and use as food for thought in your own organization.
Interface
Interface is a global flouring manufacturing company that made corporate social innovation a central part of their business strategy through Mission Zero. One of their innovations that sustained the social mission was recycling nylon from fishing nets discarded by fishers.

This led to the Net-Works program that also created a new supply chain. In seven years, they helped recycle 224 metric tons of discarded fishing nets, saved oil and reduce CO2 emissions while raising income levels for 40 communities.
Since its implementation in 1996, the strategy has reduced Interface carbon footprint by 69%, as well as waste on landfill by 92%, greenhouse emissions by 96% and increased the use of renewable energy by 89%.
With a strategy set for more than 20 years, there are lessons to be learned from their long term success: leadership plays a huge role in changing mindsets and creating a culture that fosters new thinking. In order to transform vision into action, you need to have a credible action plan.
Vodafone
Vodafone launched the mobile wallet M-Pesa in Kenya in 2007. It was a successful social innovation that provided millions with financial services, allowing them to make fast and secure payments with their mobile phones.
In the first months over 1.1 million people started using the service and $87 million had been transferred. In just two years more than 8.5 million Kenyans were using the service transferring US$3.7 billion (10% of Kenya’s GDP).
They later expanded this service to new markets in Africa. In 2013 they launched their service in India, but they failed to repeat the success from Kenya. M-Pesa worked so well in Kenya because of the early market penetration. By the time they expanded to the Indian market, startups had already started to take over. The political scene also influenced their operations as the Prime Minister announced a demonetization which was followed by a shortage of cash.
It’s interesting to draw on the lessons learned by Michael Joseph, founding CEO of Safaricom and director of mobile money at Vodafone Group. Building trust as a brand is essential when addressing a new market and expanding the same solution to new areas comes with unexpected challenges. Lessons can also be learned from their failure in India, as we can see that there are so many factors to consider in scaling a social innovation strategy.
Tesla
When we talk innovation, we have to mention Tesla. Their mission is clear: to move towards a zero-emissions future. Their model proves that sustainable is good not just for the environment but also for business.
In their 2019 impact report Tesla states that for over 550k sold vehicles they saved 4M metric tons of CO2. Their extensive charging network has saved over 75M gallons of gasoline and at the same time they are gathering data to harness the power of artificial intelligence and machine learning which allows them to improve their products and services.
Tesla proves the commitment to renewable energy not just through their cars. They, for example, brought a sustainable and affordable energy solution to the island of Ta’u in American Samoa where they created a microgrid of over 5.3k solar panels and 60 powerpack systems.
They can power 100% of the island's needs on clean energy for 3 days even if they have no sun. The 900 residents used to burn 110k of diesel every year but now they have clean and affordable energy all year round. It might not be a high profit move, but it shows that they put their money where their mouth is.
Philips
They came up with Philips Africa Innovation Hub after seeing that the African sales team was generating many ideas targeted at marginalized communities. In a traditional company structure, ideas got stuck in the middle. By creating the Innovation Hub, they enabled Philips Africa team to closely collaborate with their global R&D strategy teams.
The Africa Innovation Hubs is located in Nairobi as part of the sales unit so they can be close their customers and market insights. This is what led Philips to launch on the market a pay-as-you-go model that rents out LED lights to low-income households.
Conclusions
Now that business leaders are aware that financial goals are no longer enough for their companies to thrive, they should see the greater potential in social innovation. While CSR can still be powerful when done well, it doesn’t mean that you can’t aspire for excellence and try to improve on your targets and results.
It’s important for companies to realize that they have the power to lead the way and create positive consumer behaviour change that can improve current standards. As this is a huge responsibility to undertake, it’s also easy to fall in the trap of trying to add social value at the expense of business goals.
The approach to innovation can differ from one company to another and while social innovation might not be the only answer for your business, there are still other areas where you can start innovating.
To find out more, download our ultimate guide to different types of Innovation here.