Innovation Roadmaps – The What, Why and How
As visual creatures, we rely on graphic representations to simplify and communicate complex data. Over the past decades, processing information has become more challenging than ever, yet decision-making relies heavily on understanding and communicating this data.
So, the visual communication responsibilities also extended from specialized roles to managers and professionals who need this additional skill to make sense of their work.
This is the case because visual expression is essential not just for purely statistical information, but also for business workflows and processes. So, next to the all-too-common charts and graphs, roadmaps have become a key tool in showcasing and guiding the journey of a business, product, or project.
Even though roadmaps have been commonly used in product development, they are just as powerful as a communication tool for innovation. The versatility of roadmaps makes them highly practical in building a joint understanding and alignment between strategy and innovation activities.
There are countless tools designed to helps us visualize data, create charts, workflows, or roadmaps. However, the true challenge is not what tool to choose, but how to process, structure and organize the vast amount of data and information required for innovation activities. For this, one needs a clear mind, and a deep understanding of what it takes to simplify the complex.
To that end, we wrote this article on innovation roadmaps to explore their important role in bridging the gap between today and tomorrow. We’ll dive deeper into the types of innovation roadmaps, the challenges, and practical tips on how to make them work in your organization.
Table of contents

What is an innovation roadmap
Before getting down to the nitty-gritty, let’s take a step back and explain what an innovation roadmap is, and how it’s different from other types of roadmaps you might be more familiar with.
In short, an innovation roadmap is a visual representation that aligns the organization’s strategy with innovation actions and brings clarity to the direction, processes, priorities, and timeline required to achieve specific goals.
An innovation roadmap is a visual representation that aligns the organization’s strategy with innovation actions and brings clarity to the direction, processes, priorities, and timeline required to achieve specific goals.
An innovation roadmap has many levels of abstraction, relevant to the types of innovation or projects you pursue. You could have, for example, high level roadmaps that span over many years, or very detailed roadmaps that focus on short-term projects.
As there are so many variables, there is no pre-defined template you can simply apply to your upcoming project. And since it’s a highly flexible and adaptable tool, the most challenging thing about innovation roadmaps is the risky and uncertain nature of innovation itself.
That being said, there are certain “rules” in creating an innovation roadmap that if followed, can help you achieve your innovation goals.
First, any innovation roadmap should consider a set of clear deliverables necessary to move the organization from point A to point B. For that to happen, one must research the market, gather insights, identify trends, and white spots, and create scenarios for development of future markets, technologies, or products.
With this in mind, and a thorough assessment of the organization, you set goals, milestones, and map out a visual presentation of what your plan is.
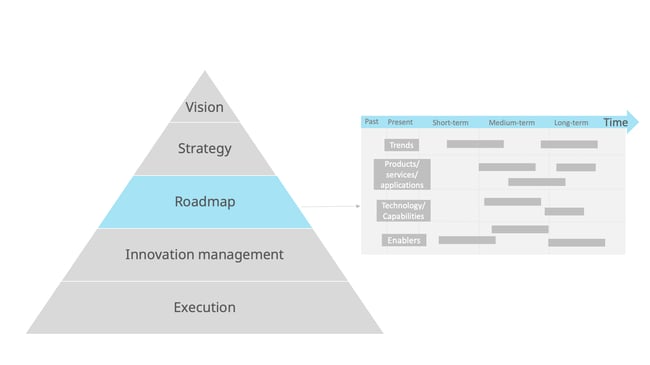 Therefore, a good roadmap should connect time: the past, present, and future, and space: the top and the bottom of the organization.
Therefore, a good roadmap should connect time: the past, present, and future, and space: the top and the bottom of the organization.
Basically, as you progress, you move both horizontally (the timeline axis), and vertically, (the organizational axis) on the roadmap. As you advance to achieve new milestones, you follow strategic goals, so you move top-down, and you work to execute innovation activities, so you move bottom-up.
To summarize, a roadmap for innovation is the link between the top of the organization where the vision and strategy are created and the bottom of the organization, where the innovation activities happen.
These innovation activities are very different for each organization and at times, for some, it might seem like a guessing game as you try to make predictions and bet on something that could take shape only in years to come.
But as is usually the case with innovation, you can’t possibly know everything in advance. So, you need to take some risks, and make the most informed decision you can, with the information you have. Of course, this also requires some resilience as you will have to adjust as you go, if things don’t turn out as planned, which rarely do.
That’s how cellphones, electric cars, and many other technologies were developed by some of the largest organizations. They decided to bet on technologies that were in their early stages and work on a long-term innovation roadmap.
With all the effort required to create an innovation roadmap, you might wonder why would an organization bother, and get distracted from the everyday business as usual? The simple answer is, because if you don’t include innovation in you “business as usual”, sooner or later, you’ll be left behind, and the business will die. You’ll either be surpassed by the competition, or you’ll be unable to keep up with the changes that took place around you, while you were busy in the everyday work.
So, there is no way around it, innovation is the way forward and innovation roadmaps can give you clarity on how to move in that direction. Let’s see how.
The importance of roadmaps in realizing innovation
Simple annual planning is what all companies do, but it can only get you so far. On one side it can be too short-sighted and on the other it can be too long to adapt to changes you go through during the year.
A good innovation roadmap balances both short- and long- term aspects. For high-stake big innovations you need a roadmap that considers the long-term vision and the short-term changes. That’s where you’ll start seeing the real value of an innovation roadmap and reap more of these benefits:
-
Align innovation capabilities and strategy
First, and foremost, an innovation roadmap brings together and aligns the business (and innovation) strategy with the innovation capabilities. Not only that, but because you can capture the bigger picture, you’ll get clarity, which in return enables the organization to implement the strategic decisions that were made.
The roadmap concerns the whole organization, even though only a selected few will work to develop it. Since it serves the entire organization, it should also make communication much easier, otherwise people will not grasp how the strategy and goals translate in practice, in their work.

Getting that broad scope early in the preliminary phase is a collaborative effort that involves leadership from different departments across the organization. For example, it’s essential that when you decide to embark on this journey you bring at the same table senior leaders, innovation leaders, head of departments like sales and marketing, engineering, and R&D.
In the assessment phase this “get-together” will help define strategic gaps, pipeline or process gaps and the skills and capabilities required in achieving the vision and goals. Just as important is to set targets and priorities to strengthen the strategic direction.
-
Manage innovation better
With the help of an innovation roadmap, you can streamline the innovation management process and methods. It might be bit of a mouthful, so let’s briefly unpack this.
In short, innovation management refers to how you handle all the activities related to innovation, from generating, prioritizing, developing and putting ideas in practice to launching new products, services or even coming up with breakthrough innovations.
It goes without saying that while on paper it all seems straightforward, if you’re someone who has ever gone through all these steps, you know how incredibly difficult it can be.
However, from our experience we noticed that organizations that manage innovation successfully have a few things in common:
- They empower and hold people accountable
- They bring together great teams on all levels of the organization
- They put in place the structures, tools and processes that make things move forward
- They follow a clear vision that is easily understood by everyone in the organization
- They have a clear focus on idea implementation
You can notice from this list some of the elements that an innovation roadmap brings to the table. In creating your roadmap, you:
- Set goals that are aligned with the vision of the organization
- Provide a clear focus on the direction in which the organization is heading
- Bring clarity by transparently communicating all these things throughout the organization.
This last point on the list leads to another big benefit of the innovation roadmap:
-
Foster clear communication
A roadmap is meant to be the product of collaborative work from different teams and departments in the organization. Of course, this can vary depending on the type of roadmap you’ll be working on, but generally speaking, you’d want to involve more than just the top managers or a single department with similar expertise.
The advantage in doing that is that you can bring together different perspectives and insights on past, present, and future. For example, senior employees can give an overview of the “scene” and bring to light the success factors of current projects in relation with previous ones.
The outcome of this work is shared with employees who will have a better understanding of the direction in which you are heading. A visual representation of the strategy, goals and milestones ahead will bring clarity to people and a sense of belonging as they all work toward realizing the same vision.
-
Shine light on the white spots
In the process of setting up the roadmap you have to research the current market, but also identify trends and based on this make assumptions on possible scenarios for the future market needs. What is the next big thing that is slowly getting traction? What components and capabilities will be required to fulfil those?
This step must not be skipped as it shines light on those white spots that if filled turn into new innovation opportunities.
For example, there is a big hype around web3, the next-gen internet that promises to revolutionize businesses from all industries, as well as our interaction and presence online. Naturally, there are many companies that see a lot of opportunities in this area as web3 has wide applicability.
The trend is still in the beginning so organizations have plenty of white spots to fill in before this technology can transform their business and create breakthrough innovation.
As some of them will work on their innovation roadmap, they will frame their problem domain and ideate on possible scenarios. They will have to ask the right questions and look for the answers.
How will this technology unfold in the future, how it would affect their organization, the way they operate or their position on the market? Are there opportunities that should be explored in more detail? Then, what capabilities they would need, how will they fill in those white spots they identified and how will they be able to adapt?
As is the case with creating something new and with innovation, getting on the web3 bandwagon could also be risky, as some believe it to be yet another internet buzzword.
Roadmapping innovation in practice
Having clarified some of the most important aspects of an innovation roadmap and its benefits, we can move forward to the more practical things. We’ll explain the most common steps in creating an innovation roadmap through the lens of several examples. Understandably, since this is a flexible tool, many of the steps will look different for your organization, to match your goals and internal structures.
So, let’s see what the key steps are in creating an innovation roadmap and how to know if they are also the right ones for your organization.
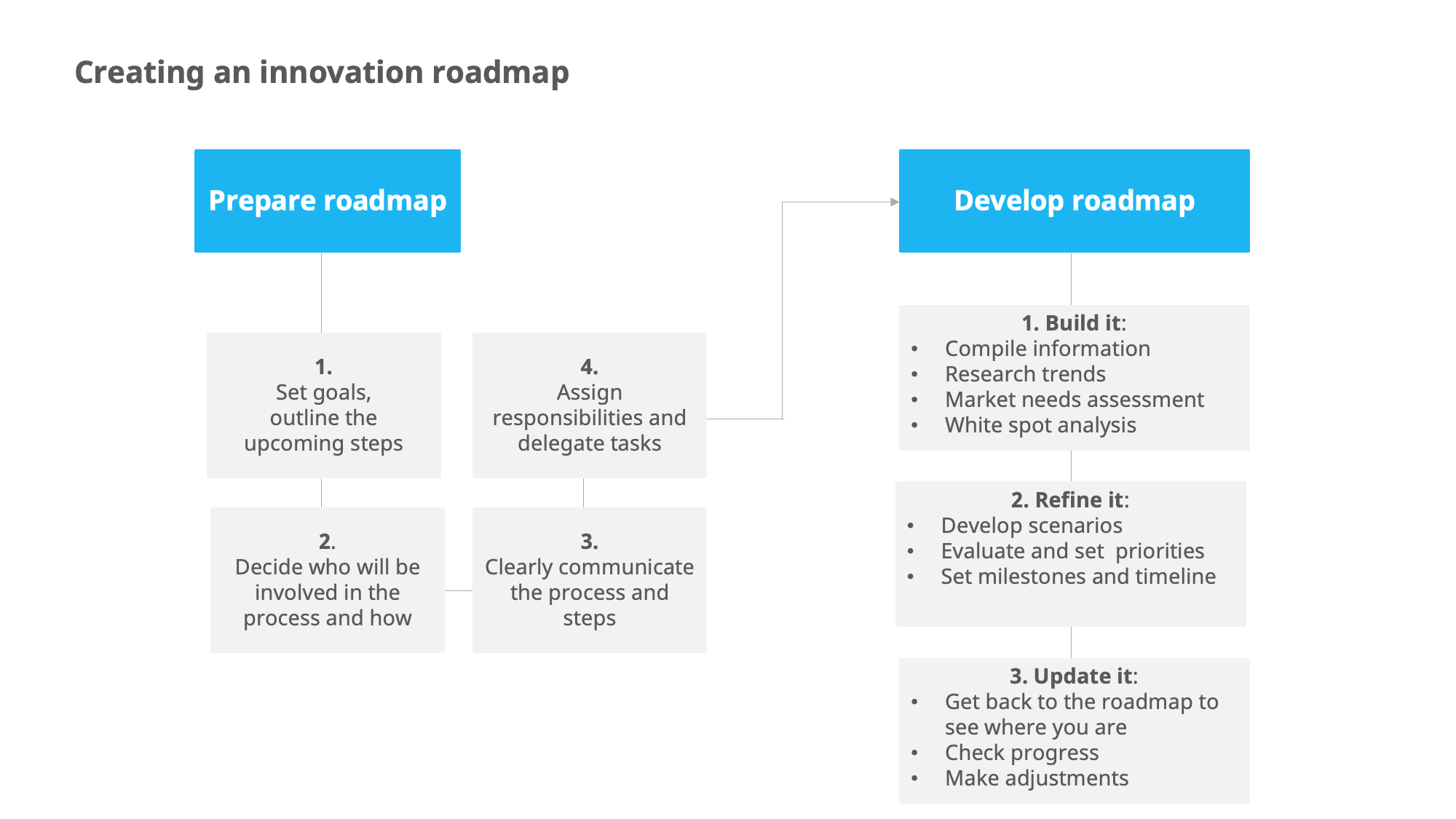
We divided this into two main parts: the preparation work, and the development work.
-
Preparation work:
For the initial setup, you need to establish the goals, problems or opportunities you will pursue through this roadmap. This applies to any kind of roadmap, whether they are high-level or more specific, at a smaller scale.
In this preparation stage you should consider the vision and strategy of the organization and how your innovation aspirations and goals could be built into that. Basically, you need to find alignment between the goals and the vision, business strategy and innovation strategy.
For example, in this roadmap for international consumer packaging, developed by researchers at Cambridge University together with the biggest companies in the industry, they started with three key goals: capture key trends in the packaging sector, communicate the implication of the trends and the opportunities for innovation, and provide a framework for strategic planning, decision making and collaboration in the sector.
In other cases, like one of these roadmaps for developing a more sustainable chemical industry, they set goals that are short, medium and long term, like: efficient removal of trace toxic metals (short-term), eliminate high risk and high impact chemicals and deliver effect with significantly lower material (medium-term), and zero impact, zero toxicity products and processes (long-term).
The roadmap can be extensive, to include many areas in the organization, or focused on a single goal. For complex roadmaps you might have several goals, that will be broken down into milestones or different project cycles.
To sum up, before rushing enthusiastically to draw charts here’s a short recap of the preparation work:
- Outline the goals and the steps that will follow in creating the roadmap,
- Decide who will be involved in the process and how
- Clearly communicate the process and steps involved in developing the roadmap.
- Assign responsibilities and delegate tasks that set the scene for the next steps. This will give participants time to “do their homework”.
-
Developing the roadmap
Next, you can start setting up the roadmap. For a better structure and more clarity, we can split this further into three main stages of setting up the roadmap: building the roadmap, refining the roadmap, updating the roadmap.
Let’s briefly go through each of these:
1. Building the roadmap:
The process of developing a roadmap can look very different for each organization but in the initial phase managers should compile information, research trends, and analyze markets. Based on these findings, they can make assumptions on future market needs and opportunities, and identify components required to develop products or services that fit their innovation goals.

This information can be developed into possible scenarios, like when would certain trends be of greater importance for your industry, what issues they could pose, and what priorities can be set to turn them into opportunities for innovation.
If we go back to our first example on the consumer packaging roadmap, we observe that after they set up their goals, they started working on a high-level roadmap that would provide guidance, structure, and context to enable innovation in the packaging sector.
They developed the roadmap by running twelve workshops that brought together over twenty companies, all important actors in the industry who provided their insights and expertise.
Your organization might not need such a big set-up with so many workshops, but getting together the leaders, decision makers and people with the right expertise is essential.
So, you can work on this initial comprehensive assessment through workshops, or if your participants are spread in different remote locations, you can run online activities like idea challenges for people within your organization, or open innovation activities for collaborations with external stakeholders.
As shown above, the foresight and assessment activities consider trends, market needs, white spots analysis, and scenarios.
Kati Pallasaho provides some useful tips on how foresight can inform your strategic decision, but also how to identify the trends which can guide these decisions. The two main principles she mentions, are adapting a wide lens, so looking beyond the changes that occurs in an organization’s immediate field, and the second is to go beyond the strong signals, so to pay attention to other details and signals than just trends and megatrends.
Remember that these are guidelines and rules of thumb rather than a “to do” list. The tools and specific steps can look different for you.
For example, if you’re working on a shorter-term innovation roadmap for an existing product, you might not need to do most of the aforementioned activities and can instead focus on customer requirements and market trends.
2. Refining the roadmap
This overview is the basis on which you build the details of the innovation roadmap. To refine it, you need to first set priorities for your innovation scenarios, activities or projects.
This can be a lengthy process, that can be again discussed and refined during group sessions, online or offline. For each priority you need to evaluate the probabilities, white spots, and capabilities required to realized them. Participants should evaluate the milestones for the short-, medium-, and long- term scenarios and decide on the feasibility and the potential for success.
This section requires involvement from many levels of the organizations, so you can setup a plan of work to define tasks and ownership for them. To guide the roadmap, it’s best to have a designated facilitator who can enhance the process.
Even though the entire process can fill tens of pages and reports, in the end you want to simplify the information into a clear roadmap that includes goals, priorities, milestones, and timeline. You can decide on the level of detail, but since an innovation roadmap should communicate the strategy and direction of your innovation initiatives, the simpler the easier to understand and act on it.
Always go back to the main goals, structure and framework of your roadmap, so you don’t get lost in the details.
For example, the companies working together with researchers on the international roadmap for packaging, started their work with the framework of a technology roadmap, that was the skeleton on top of which they built an architecture that was later filled in with their findings.
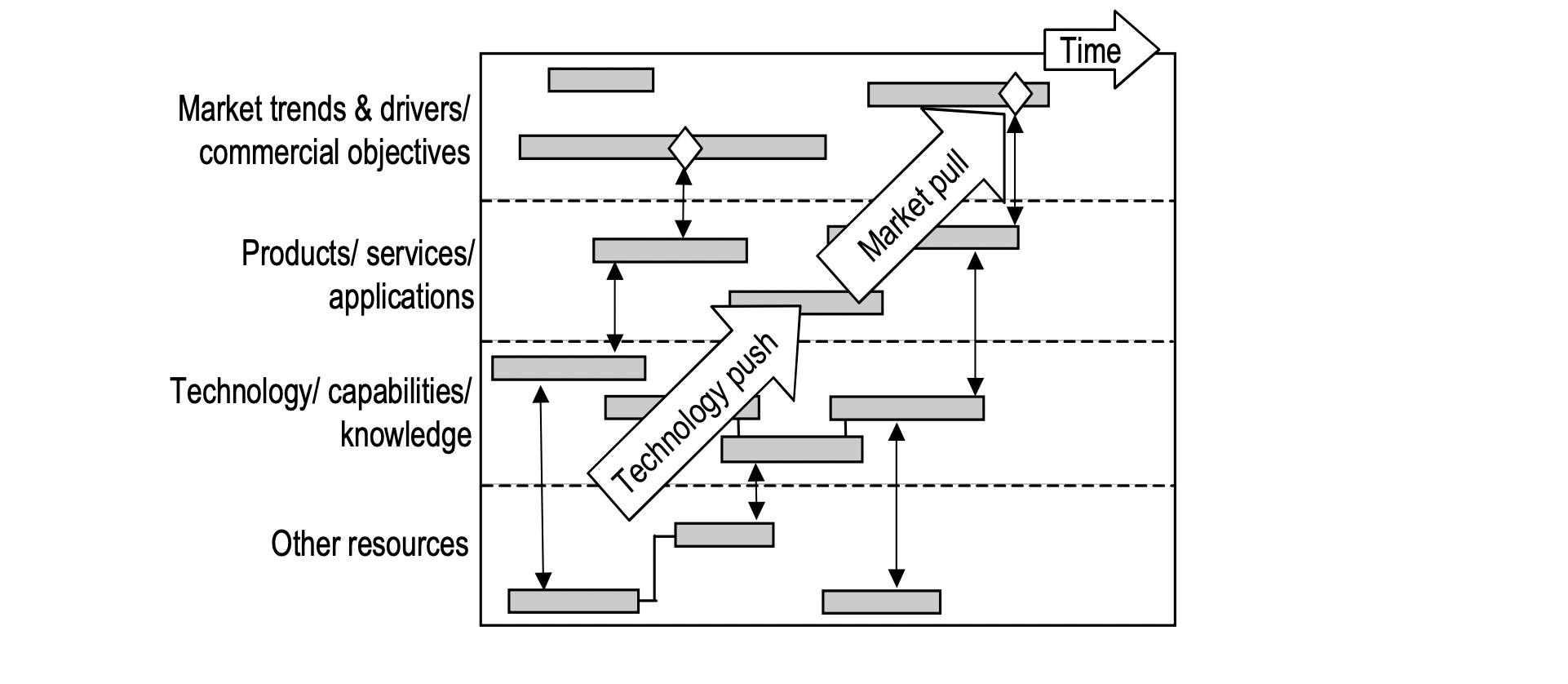
Source: International Roadmap for Consumer Packaging
3. Updating the roadmap
Last, but not least, as mentioned before, a roadmap is flexible. Part of the work involved in creating a roadmap is to identify the next milestones for removing uncertainty from your innovation activities. This means that periodic updates should be built in and tied to those milestones.
Another reason why you want to update the roadmap periodically is that markets, trends, and technologies evolve and shift all around you. After all, if we’re talking about innovation, we know that it’s constantly subject to change and unpredictability.
Since you can't prevent the unpredictable, you want to be prepared for it by including in your roadmap periodical reassessments. Revisit the roadmap after each big milestone and look at potential developments that might influence its progress.
A structured approach to updates on the roadmap can work in some situations, but it all comes down to your internal processes. If the roadmap is created around incremental innovations, the process will look different, and so will the timelines.
On the other hand, for an early-stage startup, the roadmap could have the following milestones: achieve product-market fit and secure a series A funding; Find repeatable go-to-market channels to secure series B funding; Get to positive unit economic and secure series C funding.
Each of these important milestones will require a revisit of the roadmap and adjustments according to results and progress.
Success factors
Now, based on all that we’ve explored so far, it’s time to wrap things up and bring it all together with a few key success factors for your innovation roadmap.
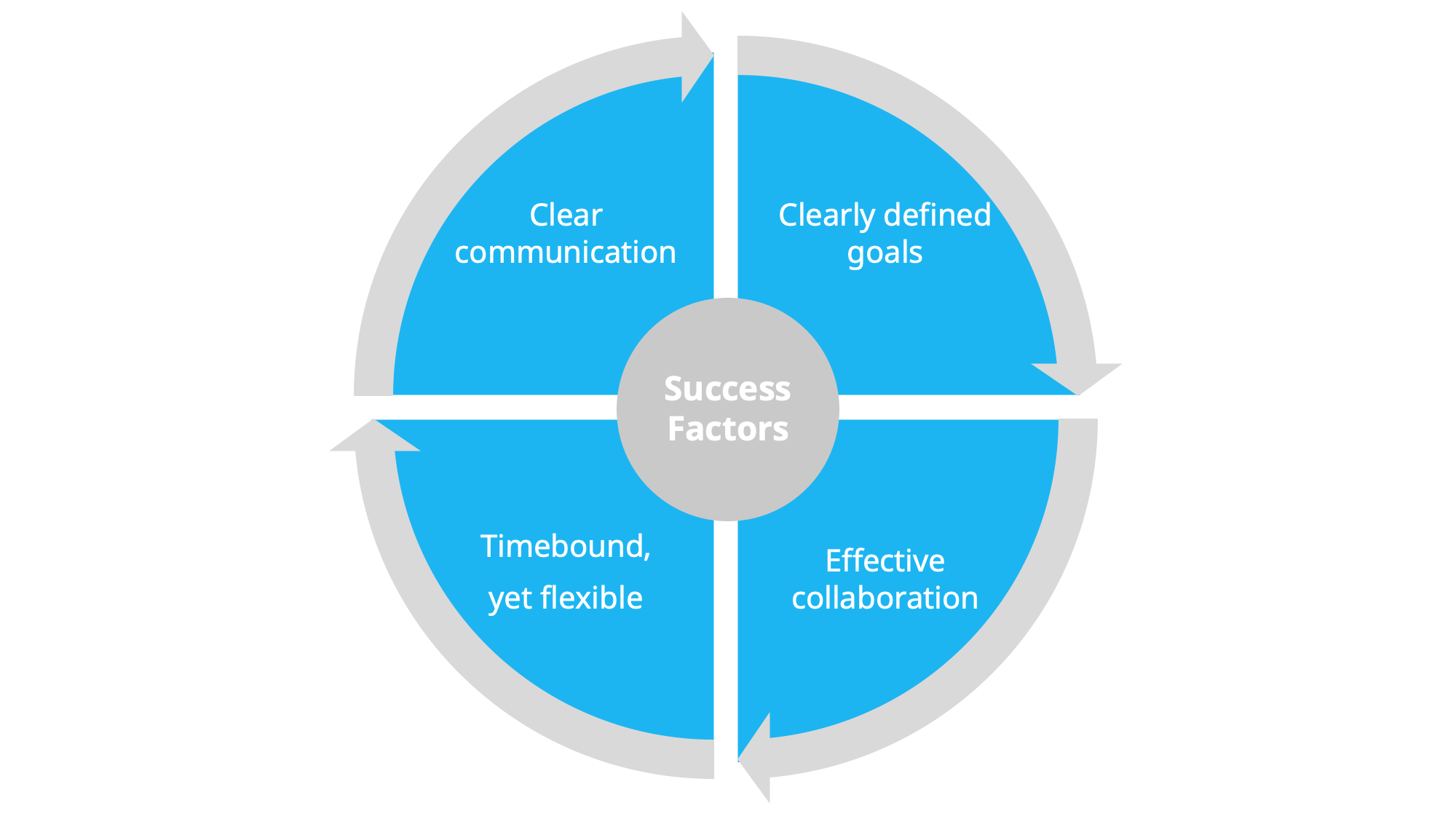
Clearly defined goals
The goals you set will dictate not just how the roadmap will look, but also the processes you’ll need to establish. As already mentioned, the goals you set have to be aligned with the overall strategy. But also, remember and remind others why you need a roadmap in the first place.
Is it to showcase your vision and excite others about it to get involved? Or is it more about internal alignment of departments? Clarifying these things early on will help you set priorities and decide on the best approach.
For example, the mobile phones industry. 20-30 years ago, people started using mobile phones, but big clunky versions, usually attached to their cars. An innovation roadmap for a phone company at that time would start with a big vision of providing users with more flexibility in using their phones. They could already see the high potential in the mobile phone industry at that time, and they know it’s an area that needs innovation.
The long-term goal was to develop the technology that would allow that. It would take many smaller medium- and short-term goals to fulfill their vision, but it all starts with clearly defined big goals and overarching vision.
Effective collaboration
As we’ve seen in the examples above, all these roadmaps are team exercises that require different perspectives. It’s crucial to encourage collaboration and participation to get new ideas and insights, but also to get their backup in pushing the agenda forward.
Here you can have both internal and external stakeholders. Internally, you want to engage leaders and decision makers. They have the knowledge and insight on internal capabilities and white spots. They also have to push the message of the initiative down to the bottom of the company where innovation is implemented.
If you’re engaging in creating complex solutions, you might need external perspective from experts that your organization doesn’t have.
Time-bound but still flexible
One of the many challenges in building an innovation roadmap is that innovation is risky and uncertain. McKinsey calls this the moving-target dilemma. Roadmaps that look farther into the future have a “moving” innovation objective because you don’t know how consumer behaviors, technology and markets will evolve.
So, you should consider the uncertainty of the future by creating flexible innovation roadmaps. You can do this by looking not just at trends in your own sector, but also at megatrends that concern your company’s future, as well as widening the lens to see what other changes can have an impact on the organization.
Clear communication
Last, but not least we come back to the most important role of a roadmap: to communicate visually the short-, medium-, and long-term goals aligned with the company’s strategy.
This is a big task and it’s tempting to include a lot of information and details. It might be about visual representation, but you don’t need a dedicated designer to draw your roadmap. Instead, you need someone who can structure information clearly, has a good overview on all the elements and can bring everything together.
You need someone who can structure information clearly, has a good overview on all the elements and can bring everything together.
However, you shouldn’t get stuck in such details, and there are also plenty of tools that can help you roadmap your processes. The key is to communicate the essence, without using too many jargon terms, so it’s easy to understand for everyone.
Conclusions
We finally reached the end of this article, and even though such a big topic can be covered in many more words, we hope you found some useful tips that inform and inspire you in your innovation work.
It might feel overwhelming to look at high level roadmaps that have thought everything through. It takes a lot of team effort, time, and work to get there, but it’s all through baby steps. You don’t have to replicate that level of complexity, you just have to start.
Remember to look at the big picture. What is it that you want to achieve with your innovation work? Can a roadmap bring clarity on your strategy, goals, and vision? After all, an innovation roadmap is a compass for your innovation journey and a practical visualization of your strategy.
Whether you know where you’re heading or you are still figuring it out, a roadmap will give your organization direction and will help uncover new opportunities to grow, innovate and ultimately thrive in the future.
If you want to increase innovation in your organization, you can use a roadmap even at a small scale to find answers to important questions. Where is your organization heading? Where are you playing, how is this background looking now and how it will look in the future, and where do you position yourself in relation with the other players? The big questions you should have in mind.