Working with our customers and partners involves a lot of interesting conversations about innovation. People often have quite many questions around it, and we've noticed that some of those are being asked more frequently than others.
Because innovation is such a broad concept that can be approached in different ways, we wanted to share some of those frequently asked questions with you to help you understand it a little bit better.

Behind the links at the end of each answer, you'll find more comprehensive information about each topic.
So, without keeping you waiting any longer, here comes the top questions and answers about innovation.
Questions about innovation management
1. How do you define innovation?
It probably doesn’t come as a surprise that innovation has an endless variety of definitions. We like the Merriam-Webster one that refers to innovation as being “the introduction of something new”.
Innovation can be a new idea, product or method that is translated into a good or service that creates value or for which customers are willing to pay. The essence of innovation is improvement – the ability to create something better and launch it to the world.
Read more: Innovation Management – The Complete Guide
2. What is innovation management?
Innovation management refers to handling of all the activities needed to “introduce something new”. From an organization's perspective, it means things like employees coming up with new ideas, developing, prioritizing and implementing them, as well as putting them into practice.
Innovation management is simply the continuous process of coming up with and introducing new improvements and developing the business, one way or the other. This can be done for example by launching new products, or by introducing new, improved internal processes.
Read more: What is innovation management?
3. How do you approach innovation?
Innovation can be approached in different ways, however, we recommend taking a holistic approach to it that takes into account different aspects of innovation.
Through our experience in helping organizations with their innovation activities, we’ve found that the simplest way to understand these aspects is to break them down and discuss each of them separately.
We typically approach innovation through the following ones:
- Capabilities – The abilities and resources an organization has for creating and managing innovation, such as skills, knowledge and financial capital.
- Structures- The organizational structure and processes that enable the effective use of capabilities.
- Strategy – The plan an organization has for achieving long-term success.
- Culture – How things are done in an organization, organizational values, ways of working, etc.
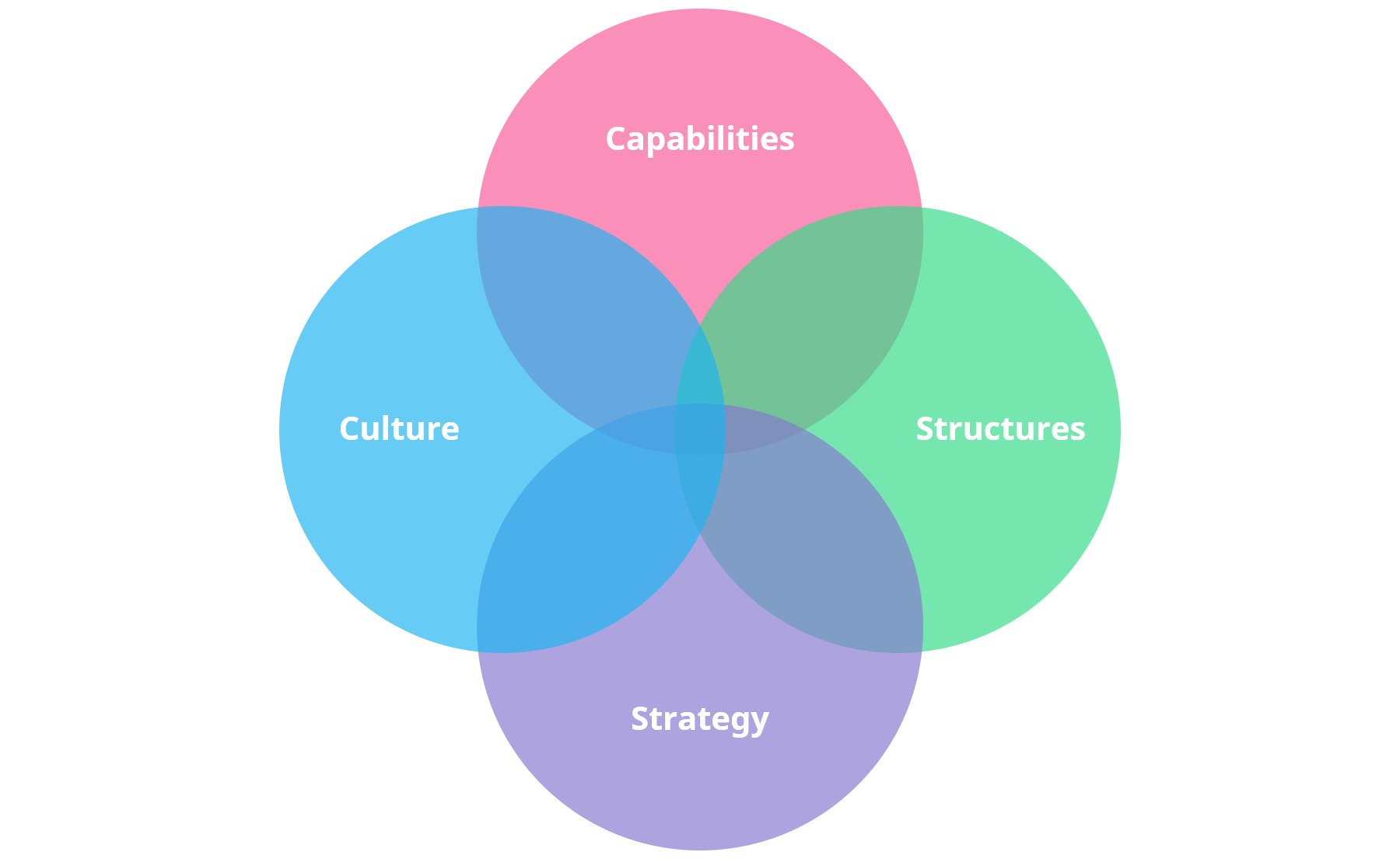
What we mean by taking a holistic approach to innovation is to consider each of these four aspects when innovating. It's not enough to do well in just one of these areas as you need all of them to work in order to succeed.
Read more: The Key Aspects of Innovation Management
4. Why does innovation matter?
When looking at innovation from a society’s perspective, it is one of the sources of economic growth, collective well-being, education and environmental sustainability.
The world around is changing in a fast pace and the ability to innovate, adopt new innovations and learn how to use them, is inevitable if you want to stay relevant and keep up with those changes.
Read more: The Importance of Innovation – What Does it Mean for Businesses and our Society?
5. How do you succeed in innovation?
There are many ways to innovate and success depends mainly on the individual aspects such as the market you’re operating in, as well as the unique capabilities of your organization, just like in business in general.
It's not smart to slavishly follow other's success stories because what may have worked well for someone in the past, might not work for you.
When speaking about innovation, there’s no guarantee that previous success will automatically repeat itself as success depends on a number of other factors as well, such as timing and structural aspects of your organization.

There are, however, some practices that might be useful for a majority of organizations:
- Strive for constant improvement – Innovation is about constantly improving and looking for ways to do things better both as an individual and as an organization. You need to make small, continuous improvements to succeed in the long run and often the biggest innovations result from those smaller innovations.
- Keep creating value for your customers – From organization’s perspective, innovation is just another tool for creating more value for your customers.
- Empower people but hold them accountable for their work and their decisions – Succeeding in innovation is about finding the right balance between freedom and control.
- Have talented people on all levels of the organization – Skillful people with innovative mindset is what makes you and your company unique. Find people who have the ability to have a critical but open-minded approach on innovation and are willing to learn and make concrete changes happen.
- Have tools and structures in place for making sure things happen and the right things move forward – It’s the concrete, everyday ways of working that define your potential to succeed.
- Have a clear vision and a strategy that everyone understands – To be able to make innovation happen, your company culture should reflect those values and they should be clearly communicated.
- Focus on implementing ideas as opposed to just talking about them – Actions speak louder than words and the sooner you're able to start, the quicker you'll start seeing some real results.
Read more: 6 Best Practices and Key Success Factors for Innovation Management & What Does Successful Innovation Management Look Like?
6. Why is innovation so difficult?
There are as many reasons for innovation being difficult as there are organizations, each of them having their individual problems to solve.
Often, the issue is that companies aren’t used to managing different kinds of innovations, they’re missing some of the critical capabilities required to innovate or they experience cultural challenges.
Sometimes, more practical things such as the organization’s structures might work as a blocker to innovation. One cause for failure can also be the lack of skill and courage that is needed to fix the blockers of innovation before it’s too late.
What makes innovation difficult is the fact that creating something new almost always involves some level of uncertainty. You don't really have any instructions to something no one has ever worked with before, which is why there is no ready manual you can use for innovation.
New innovations are always in a "delicate state" in a sense that you need to get several aspects right at the same time and just one wrong decision might ruin it.
Read more: Why Is Innovation So Hard? & Common Challenges in Innovation Management
7. What is innovator’s dilemma?
Innovator’s dilemma is a well-known concept introduced by Clayton Christensen in 1997 that explains the common phenomena related to innovating at an established organization.
It sheds some light on why highly successful incumbents get disrupted.
The core of the dilemma is that in the beginning innovation, and more specifically the disruptive kind, is usually inferior to existing products and services on the market if measured by the same metrics and value drivers.
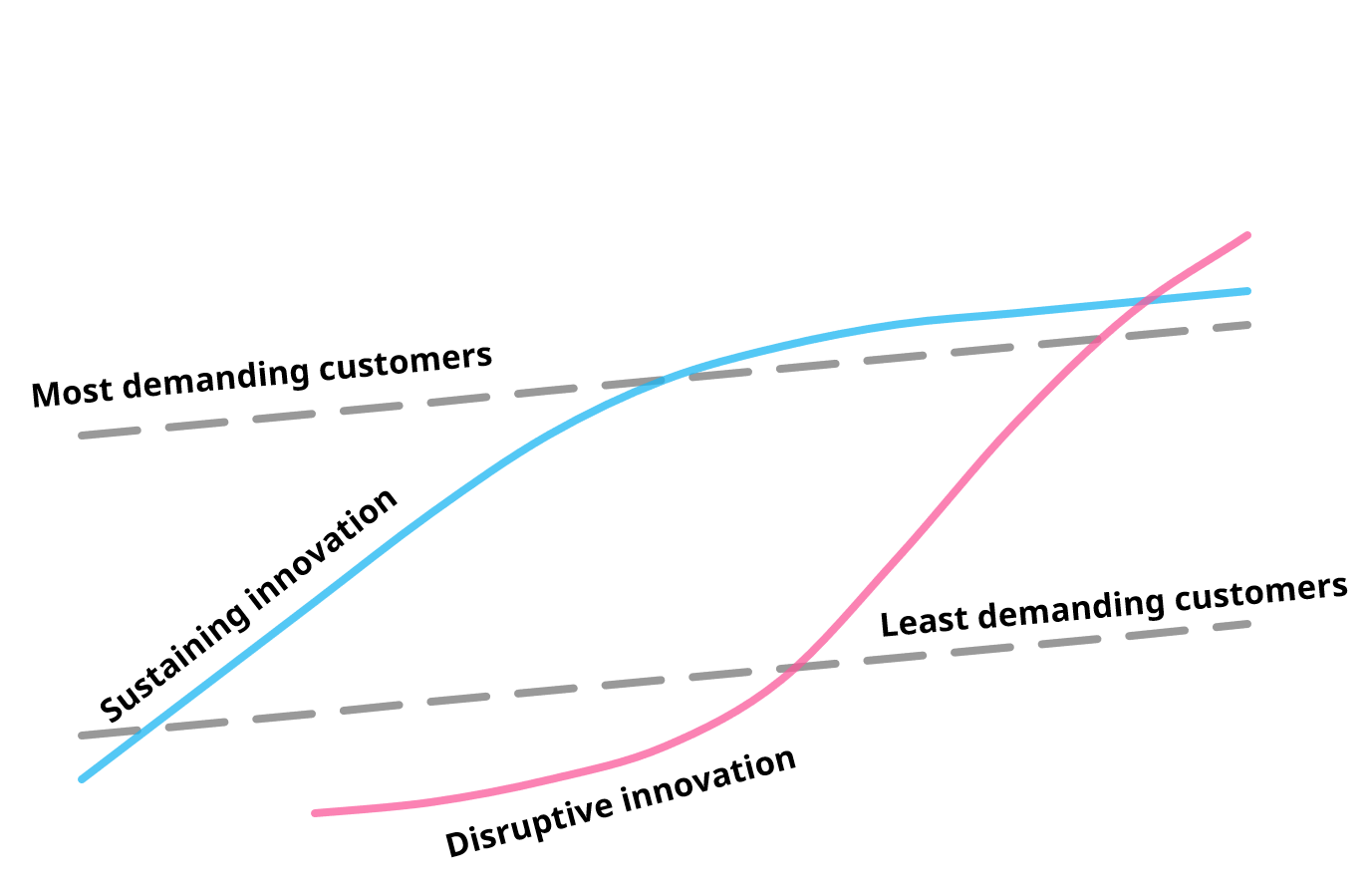
Thus, new products are initially valuable only to a small subset of the market with different value drivers and won’t be of interest for the mainstream or high-end customers, which is where the incumbent companies typically have higher profit margins.
Because disruptive innovation initially caters to only a small and not-very-profitable customer base, the rational decision-making processes of the established companies are obviously biased to not invest in these disruptive initiatives in the early stages.
Once the disruptive innovation enters the mainstream, the established companies typically pick up on them again, however at that point it’s often already too late since the new entrant is on the exponential part of the S-curve. This makes catching up quite unlikely, even with the additional resources the incumbent has at their disposal.
Read more: Innovator’s Dilemma
8. How can you make innovation a little bit easier?
Innovation doesn't have to be rocket science. Instead of getting too caught up with the challenges of innovation, there are also some things you can do to pave the way for innovation.
Based on our experience by following a few simple steps, you can make innovation a little less difficult within your organization, no matter your current level.
- Set clear goals that are aligned with your strategy
- Have a big goal you’re ultimately aiming for and then break it down into smaller, more achievable milestones
- Constantly enhance your organization’s innovation capabilities
- Keep the customer at the core and create value
- Build an innovative culture by promoting active collaboration
- Find balance between short- and long-term performance
Read more: 7 Simple Steps for Making Innovation Less Difficult
9. How do you build a process for innovation?
Figuring out the right innovation management process, or processes, can be a challenging effort. As innovation is, by nature, highly unpredictable, one way to see how a certain process could work for you is to try it out in real life.
Not all processes suit every organization and choosing the right ones depends on a number of things, such as your goals, the way your organization currently operates and the business and industry you're in.
If you’re working in a larger organization, you’ll almost inevitably need more than just a single process for the different types of innovations in different parts of the organization, so there’s no point in trying to fit everything into one innovation pipeline.
For more practical examples on how to structure the way you collect and develop ideas, I recommend taking a look at our guide to idea management processes.
Read more: Innovation Management Processes – Figuring Out the Right One
10. What is an innovation program and how do you build one?
Innovation program is an umbrella term for programs and projects that organizations create with the goal of creating new innovations and building their innovation capabilities.
The term is often used to refer to individual projects, but we prefer to think of innovation programs as the portfolio of individual initiatives such as innovation labs, intrapreneur programs, centers of excellence (CoE), accelerators and idea challenges that aim to make more innovation happen.
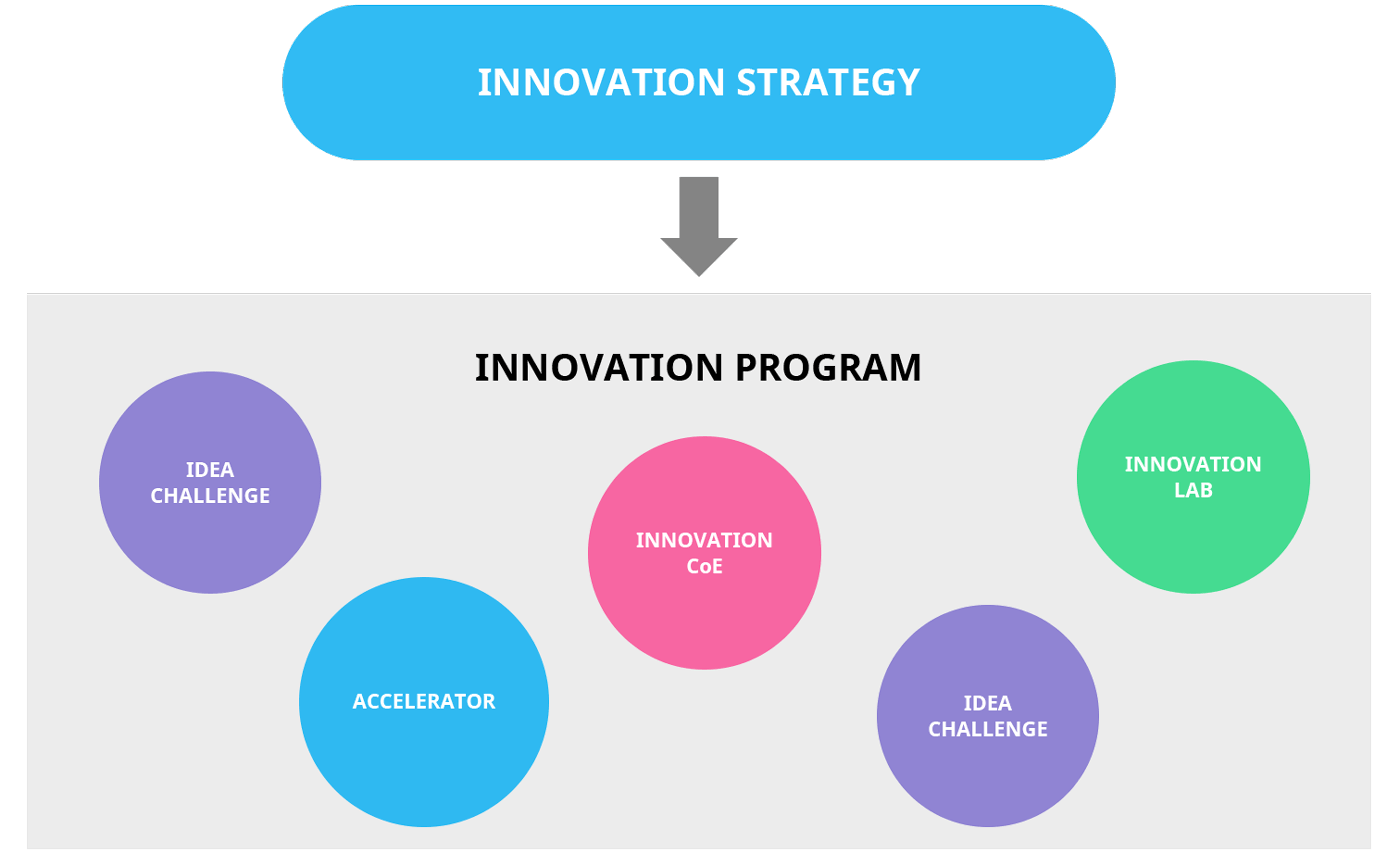
Read more: What is an innovation program?
While there's no silver bullet, taking a systematic approach to it can help you create a scalable machine for driving sustained innovation performance. To do that, you might want to watch our webinar in which you’ll learn about:
- Why so many innovation programs don't succeed
- Practical tips to building an innovation program
- Best practices for getting started with the program
- Building the momentum once you're off the ground
11. Where do innovation programs go wrong?
Whenever we talk to executives and ask how their past innovation efforts have succeeded, we usually get quite a muted response.
Most have tried at least some innovation initiatives or programs, and many have had positive experiences from some of them, but overall the end result often seems to be a bit of a disappointment.
What makes it difficult is that for an innovation program to be successful, the organization has to get a lot of things right, while still adapting to their individual circumstances.
Here are some of the findings we’ve made based on a number of different studies. You'll find more information on this particular study behind the link below.
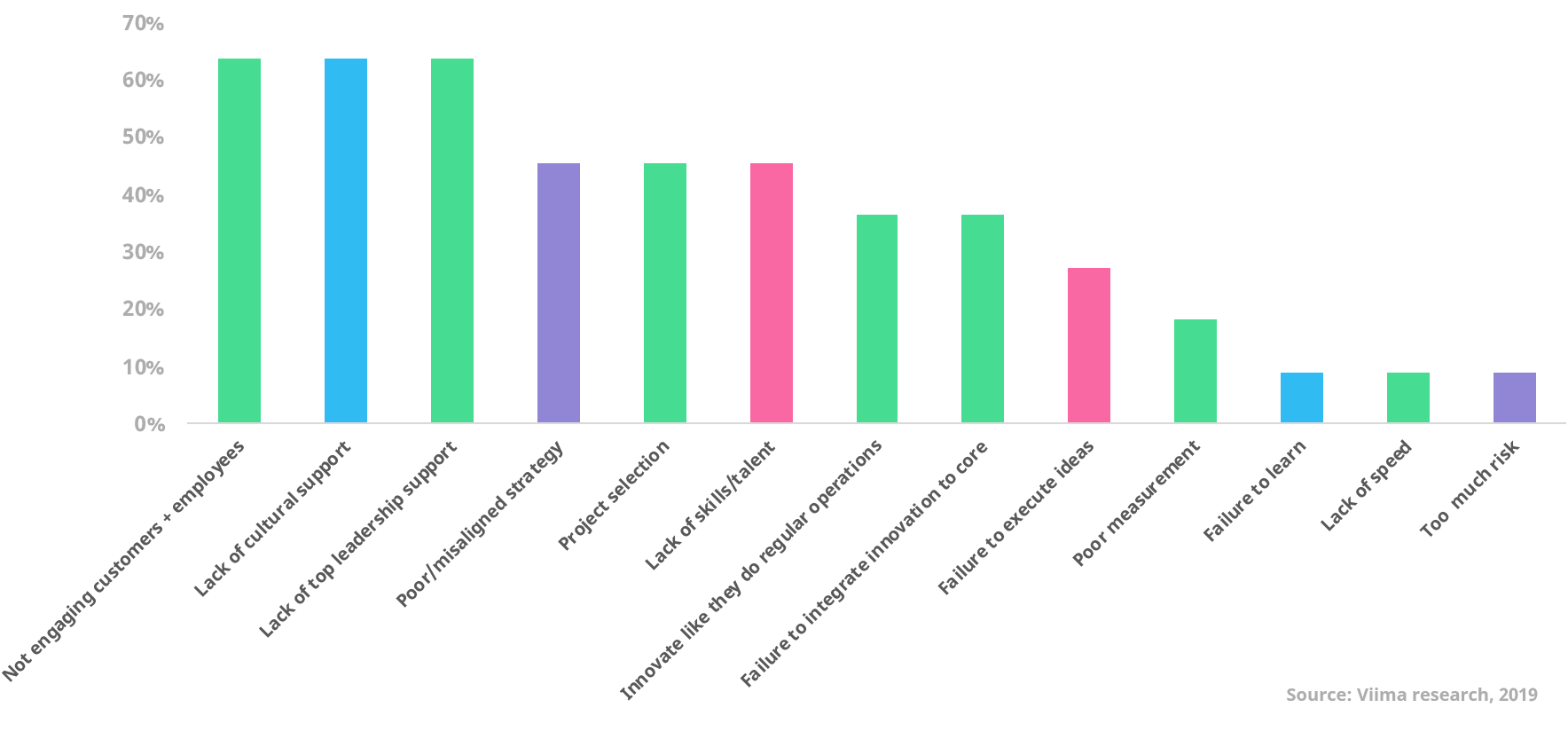
Read more: Why Do So Many Innovation Programs Fail?
12. What is an innovation strategy and how do you create one?
Strategy is about making choices between a number of feasible options to have the best chance at winning.
Innovation is just one of the means to achieve your overall strategic company goals now and in the long term. When the big picture is clear, you can take a closer look at how your organization should innovate to achieve that grand goal.
To develop your strategic approach to innovation, you should:
- Determine your objectives – What do you want to achieve and why?
- Understand your company’s competitive advantage – What’s your unique value proposition?
- Know your market, customers and competitors – What field are you playing in?
- Develop your core innovation capabilities – What are the skills required to achieve competitive advantage?
Read more: Innovation Strategy – What is it and how to develop one?
13. How do you measure innovation?
The purpose of measuring innovation is quite simple: to see where you’re standing at the moment and to ensure you’re going to the right direction. Innovation metrics allow you to see if you’re doing enough of activities, and more specifically, enough of the right kinds of activities to be able to achieve desired results.
Metrics have a huge impact on behavior, which is why it's important to try to analyze how your KPIs drive your employees' behavior.
Innovation metrics are typically divided into two different categories: input metrics and output metrics. In other words; what goes into your innovation process and what comes out of it.
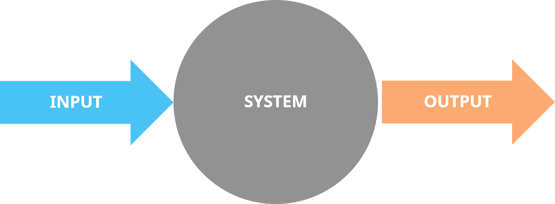
To get the most out of your innovation metrics, we recommend you to:
- Focus on a few metrics at a time
- Find a good balance of different metrics
- Prioritize the ones that are the most relevant at the moment
- Align with strategy
- Assess the maturity and uncertainty of the innovation
- Don’t force the same metrics for everyone in your company
- Use as an opportunity to learn and improve
Read more: Measuring Innovation – The Definitive Guide to Innovation Management KPIs
14. What theories and frameworks can you use to classify innovation?
Innovation management is a diverse topic with many different layers and several different models, theories and frameworks that can be used to classify different types of innovations and explain common regularities.
Understanding some of the commonly accepted innovation models and theories helps make sense of the complex topic.
While none of them can capture the essence of innovation alone, and although some of the models can be (and have been) criticized, they allow you to form a pretty good overview of the subject.
We’ve listed quite a few of them in our previous post about Key Innovation Management Models and Theories and Types of Innovation – The Ultimate Guide with Definitions and Examples
15. What is open innovation?
Open innovation is a form of innovation where knowledgeable and creative individuals who work outside the company, or, in a different team, can also contribute to achieving strategic goals through innovation. Sharing intellectual property both ways can often be useful for different parties in different ways.
More information is often better, however, it has also been proven that good ideas may become mediocre or even die if you rely on too many opinions.
So, instead of automatically inviting everyone in the open process, you should make sure open innovation is a suitable method for your specific case and engage only those who are actually relevant.
Often, companies use open innovation to:
- Engage larger audiences
- Engage relevant audiences
- Improve cost efficiency
- Involve their customer in their R&D process
- Improve PR & brand value
- Find new talent & partnerships
Read more: Open Innovation – What It Is and How to Do It
16. What are some real-life examples of open innovation?
There’s plenty to be learned from companies who’ve been using open innovation to get more ideas from different groups of people.
What comes to open innovation cases, only the sky is the limit. Some might use open innovation to add value to their hardware, while others use it to gain more information for developing new products, for example.
Netflix, for example, launched an open innovation challenge called Netflix Prize in 2006, that was open to anyone from the public as long as they were not professionally affiliated with Netflix.
The intent of the competition was to find a filtering algorithm that improves user movie or series suggestions by 10% compared to the existing one. For the winner of the competition, Netflix offered a grand prize of 1 million USD.
In just over a year, over 40,000 teams from 186 countries had entered the competition and in just under 3 years, two teams had found a way to improve the suggestions by over 10%.
You'll find other interesting examples and key learnings from a wide range of companies using open innovation in different ways behind the links below.
16 Examples of Open Innovation – What Can We Learn From Them & Types of Open Innovation
17. What are some of the challenges in open innovation?
Although open innovation has become a popular way for different sized organizations to innovate, there are also some challenges they face when implementing it.
Often, the more people you involve in the innovation process, the more there is to consider as the discussion has to be facilitated to remain active, relevant and fruitful.

The most common hurdles to open innovation can be categorized as either strategic, operational, legal or cultural.
- Strategic challenges and limitations
- Unclear goals
- Wrong type of audience
- Opportunity cost
- Operational and structural challenges
- Building an effective process
- Developing and implementing ideas
- Finding the right open innovation platform
- Legal challenges
- Intellectual property rights
- Terms and conditions
- Cultural challenges of open innovation
- Negative attitudes towards open innovation
- Lack of commitment
- Rewarding and motivating participants
Read more: Open innovation challenges – How to overcome the most common ones?
18. How do you succeed in open innovation?
Based both on our own experience working on open innovation with our customers, as well as the successes of some of the biggest companies in the world, we’ve identified some key success factors for open innovation:
- Have clear goals
- Facilitate the collaboration
- Be transparent
- Reward participants
- Find the right communication channels
- Commit to what has been agreed upon and to the goals that have been set
No matter how big or small your group is, it’s important to first understand how open innovation can help achieve the goal you’re aiming at, when to use it and why.
Read more: 6 Key Success Factors for Open Innovation
19. What are some innovation tools and resources?
Because innovation is already challenging in itself, it really doesn't make sense to spend time on reinventing the wheel. Instead, you can use some of the existing tools that have proven to be great for creating something new.
We’ve combined some of our favourite innovation tools in one toolkit and have categorized the tools based on the following themes:
- Strategy tools
- Process tools
- Idea generation and validation tools
- Idea management software
- Additional material related to innovation
These practical tools help turn knowledge into concrete actions and make the most out of your innovation journey. Because we strongly believe that shared knowledge is the best knowledge, we highly recommend sharing these tools with your colleagues to achieve the best outcome.
Learn more about how to use the toolkit: Innovation Toolkit – Tips, Tools and Templates for Managing Innovation and click the link below to get your own copy!
20. Where can you find a list of innovation related terms?
If you are new to innovation, the terminology around it might feel slightly overwhelming.
Thus, we've gathered over a hundred innovation-related definitions and terms in one place to explain what each of them really means.
Innovation Glossary – 100+ Innovation Related Terms and Definitions
21. Where can you find some quotes on innovation?
“If I had asked the public what they wanted, they would have said a faster horse. “ – Henry Ford
You might have come across this particular quote in different contexts and let me tell you – there are plenty more!
What’s great about these types of quotes is that they are a fun way to learn about innovation through the minds of those who have done it successfully or understand what it’s truly about.

People use quotes to justify their own views and to appear sharp as i can be difficult to explain cause and effect relationships. Therefore, you should be familiar with these common quotes not only in terms of learning but also in terms of clarity.
We’ve picked our favourite ones to help you reshape your existing understanding on different areas of innovation. Perhaps you can even learn something new from them.
Read more: 50+ Innovation Quotes and What They Can Teach You
22. Where can you find some statistics on innovation?
We often get asked for all kinds of numbers and statistics regarding both our clients, as well as the industry in general. Due to confidentiality, there isn’t unfortunately much of the prior we can share.
There is, however, quite a bit of data that we’ve gathered to shed some light on some of the more common themes and challenges related to innovation. We’ve broken findings from more than 20 studies down into a number of different areas and have also combined the most interesting ones into an infographic.
Read more: 50+ statistics on innovation – What do the numbers tell us?
Questions about idea management
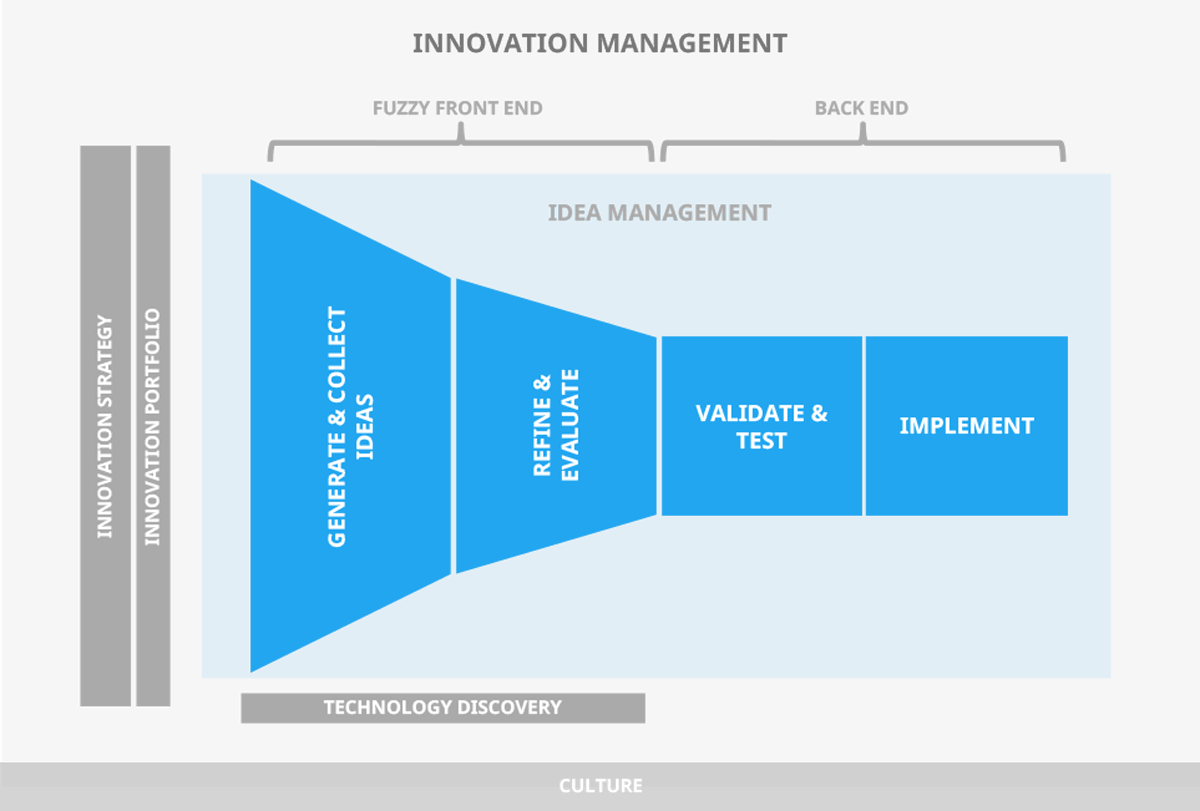
23. What is idea management?
Every innovation starts from an idea, so without them there wouldn’t be innovation.
For an organization to increase the probability of succeeding in innovation, it simply makes sense to try to collect a large number of different ideas, and then to manage and develop them effectively.
Innovation management refers to the systematic management of introducing anything new for the organization and as such, it’s a vast field encompassing a wide variety of activities, idea management being one of those.
Idea management, in turn, can be defined as systematically managing the process of collecting and developing ideas and insights to get the most value out of them.
Read more: Idea Management Defined – The What, Why and How
24. What is idea generation?
Idea generation is the process of creating, developing and communicating ideas, be they abstract, concrete, or visual. It’s the front-end part of the idea management funnel and it focuses on coming up with possible solutions to perceived problems and opportunities.
There are many ways to generate more ideas. You can, for example collect them from your employees or use different techniques for coming up with them.
New ideas can help you move forward if you feel stuck with a task or are unable to solve a certain problem. If you’re suffering from a creative block, there are some useful techniques that might be worth giving a shot to challenge conventional thinking.
- SCAMPER Technique – A holistic way of applying critical thinking to modify ideas, concepts or processes that already exist.
- Opposite Thinking – A technique that can help you question long-held assumptions related to your business.
- Brainstorm Cards – A tool that helps you consider external factors such as: societal trends, new technologies, and regulation in the context of your business.
- Analogy Thinking – A technique for using information from one source to solve a problem in another context.
Because you're likely going to need different kinds of ideas, try testing a few different idea generation techniques to see which ones work the best.
Most of these ideation methods can be used for more effective brainstorming but can also be used for other type of ideation purposes.
Read more: Tools and techniques for generating ideas
25. What is an idea challenge?
An idea challenge is another ideation technique, a focused form of innovation where people are challenged to come up with new ideas around a specific theme.
It is basically just a way of focusing ideation to effectively collect ideas in insights from your target audience.
Idea challenge is often limited by time after which the most potential ones will be refined and developed further.
Read more: The Complete Guide to Idea Challenges
26. How do you generate more good ideas and avoid the bad ones?
This is a question we hear quite often, but isn't quite right, because when you’re doing something new, you usually can't tell the good ideas from the bad ones beforehand.
Raw ideas are usually far from perfect, but people usually come up with that idea for a reason. So, you shouldn’t worry too much about getting bad ideas but to focus on the problem or the opportunity instead.
Even the worst ideas can lead to accelerated learning and you discovering something important about your business. The key to finding the diamonds in the rough is to get plenty of ideas and to have an effective process for identifying the most promising ones and managing them. Here, a solid idea management tool can help.
Read more: How to get more good ideas and avoid the bad ones?
27. What is idea evaluation?
Idea evaluation is an important tool for making better decisions. It allows you to prioritize a number of different ideas and choose the ones to pursue.
There are several different ways in which you can evaluate your ideas. It’s typically best to get as many people to evaluate the ideas as possible, as long as they have the necessary background information to be able to accurately do so. This provides you with more data points to use as the basis of your evaluation.
Different kinds of ideas need to be evaluated differently, which is why your idea management process should also take these differences into account.
Read more: Idea evaluation – What is it and how should one do it?
28. What is an idea management process and how do you build one?
While you might think that you don't have an idea management process, you actually always do. Every company has ideas and every company makes decisions on how to proceed with these ideas, one way or the other.

By defining a process for managing ideas, you'll introduce clear responsibilities that will hold people accountable for progress, as well as create a set of common rules that make the process transparent and understandable for everyone.
Typically, the processes of successful companies can be divided into three categories:
- The Centralized Model – Employees come up with ideas and put them into a transparent system, after which the idea is then collaboratively developed further. Decisions are then made in a steering group meeting or similar, which gathers in regular intervals, on whether the ideas are to be implemented or not.
- The Decentralized Model – The second is actually quite similar to the first one. The only difference is that there's no central steering group making decisions about the ideas, but the responsibility for different kinds of ideas lies with a manager (or individual) responsible for that specific area.
- The Hybrid Model – This process involves many separate processes, often including both of the above. Most big companies fall into this category.
Read more: The Ultimate Guide to Idea Management Processes
29. What is idea validation?
Idea validation is the process of gathering evidence for the feasibility of ideas through experimentation to make fast, informed and de-risked decisions.
The purpose of idea validation is to expose the idea to the real world before you spend a lot of time and money perfecting your final product or offering.
New ideas always have plenty of built-in assumptions and if some of them prove wrong, it can destroy your plans at once. Validation reduces the risk, speeds up the delivery of a value-creating service in the market, and minimizes the costs.
Although there are multiple different ways to validate an idea, the overall validation process is quite simple and straightforward:
1. Define goals and identify assumptions
2. Develop a hypothesis
3. Conduct experiments
4. Analyze results to validate your idea
Read more: Idea Validation: Steps and Tools for Testing Your Idea
30. How do you find the right business idea?
Finding the right business idea can be demanding because you need to make a decision and stick with the idea long enough to make it work.
While the exact business idea matters less than most people think, picking an idea that you’re willing to stand behind of for years, is very important. You need to have confidence in your idea to be able to convince others to trust you, which you’ll need to do over and over again on your entrepreneurial journey.
There’s a simple five-step process you can use for finding an innovative business idea:
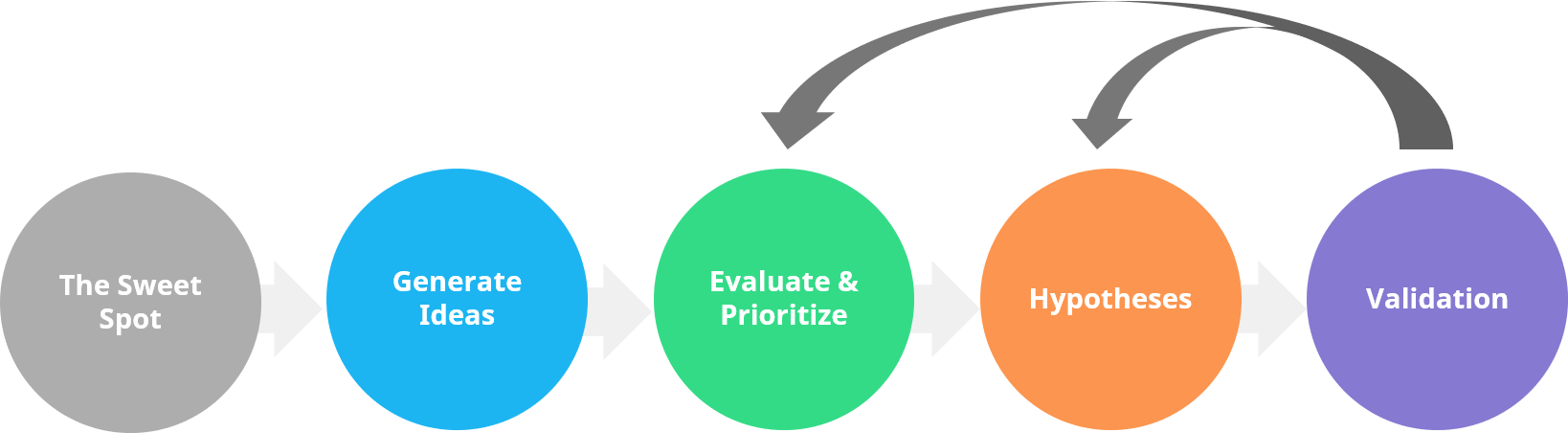
The first part of the process of finding the right business idea is to think of ideas that have the most potential. Your ideal business idea is something you’re good at, passionate about, and something people are willing to pay for.
Once you have an idea of what type of business ideas you’re looking for, it’s time to start generating them. When you have enough of potential business ideas, you need to evaluate and prioritize those to figure out which of them is the most potential for you to pursue.
You want to look for things that people are used to paying for, consider your ability to execute the idea as well as, how innovative the idea actually is. To test the idea, create hypotheses for obstacles and your key assumptions.
Keep in mind that the bigger the challenge or the opportunity, the higher the required investment and the involved risk are likely to be, which makes it even more important for you to do your homework properly by validating the idea.
Read more: 5 Simple Steps for Finding the Right Business Idea
31. How do you promote active collaboration and improve the participation rates in ideation?
Wouldn’t it be great if all your employees kept generating ideas at a consistent pace and volume?
This, however, is rarely the case as participation tend to fall if active participation and collaboration isn’t facilitated, or if the nothing seems to come of the ideas.
To improve the participation rates in ideation, you should focus on solving real problems or tackling interesting opportunities. You need to communicate the expectations clearly:
- Why do we ideate
- How do we do it and
- What are we looking to achieve with it
Some people might be reluctant to come up with and share new ideas, especially in organizations where the culture or incentives inhibit innovation and openness. In this case, it’s important to show that you listen, and will actually use the ideas to drive real progress in the company.
It’s also important to actually progress the ideas to maintain active participation. Some ways to do it is to give people responsibility, reward them and make ideation a part of everyday work.
Read more: Achieving and sustaining high participation rates in ideation
Questions about culture
32. How do you define company culture?
A simple definition of company culture is 'the way in which things get done in an organization, especially when the boss isn’t around.'
Culture is a combination of implicit and explicit rules and norms that help determine people’s behavior and responses to certain situation.
To define your company culture, you should start by assessing your current state, establish your vision, and remove any blockers that might be standing in the way of creating an innovative culture. This can be done by establishing new practices and communicating and reinforcing these new values and ways of working.
Don’t underestimate the impact of structures and incentives on company culture as these drive change and bring it immediately into practice.
Read more: Company Culture Defines You - But How Do You Define It?
33. How do you build an innovative culture?
Culture is often seen as the number one hurdle to innovation as it’s one of the slowest things to change, deeply ingrained and often tacit. It’s a lot easier to pinpoint and remove inefficiencies in processes, for example, than it is to transform corporate culture.
There are as many reasons as there are teams for why culture can become a barrier. Just like with organizational capabilities, personnel decisions related to hiring the right people is critical to culture in all organizations. To strengthen your values, you need to carefully consider who will be hired and fired, who will be rewarded, and on what grounds.
Creating a culture of innovation requires leadership and people skills, a shift in mindset as well as concrete actions to reflect these new values. Based on my experience, here are some common barriers related to culture that may slow things down:
- Lack of systematic plan for dealing with objections
- Impatience
- Not enough repetition that new habits would stick
- Lack of leadership support
- Lack of concrete structures (processes, incentives) to anchor the new culture
Based on what we’ve seen, there are two approaches to shaping culture: top-down and bottom-up. The top-down approach starts by redefining the mission and values of the organization, then seeks to cascade the changes to the organization at large.
The bottom-up model approaches the problem from the opposite direction. It starts from the people, processes and the informal ways of working, identifying barriers to change and fixing those one by one.
The solution, is to simply use both approaches, and to start making change happen across every level of the organization by:
- Communicating the purpose
- Managing both up and down
- Setting goals and KPIs for directing the work
- Being respectful
- Using hard evidence to show how change is inevitable to solve certain challenges
- Making sure the structures and processes aren’t hindering change
Read more: Top-down or Bottom- up – How to Build and Innovative Culture
34. How can you motivate creativity?
Motivated and creative employees tend to be much more efficient and proactive compared to those whose motivational needs are ignored.
They tend to seek for better ways to complete their tasks and are quality oriented. Thus, motivating creativity contributes to the overall quality of things done at your company.
But how do you actually do it?
Instead of thinking about extrinsic motivators, such as monetary awards and bonuses for those that are effective and punishments for those that are not, a lot more cost effective and sustainable way to motivate your employees is to do it intrinsically.
The main sources of intrinsic motivation are meaningfulness, responsibility and sense of ownership of your work, competence and confidence as well as making constant progress even when facing obstacles.
To enhance intrinsic motivation among your employees, look for ways to inspire them, show them trust and respect and provide them with the support they need to learn, get better and reach their goals.
Read more: Motivating Creativity – The Why and How of Intrinsic Motivation
Have a question?
We hope you found some answers to your questions on innovation. If there’s a topic we haven’t yet covered and you have a specific question in mind, let us know and we’ll answer it!
In the meanwhile, if you'd like your organization to be more innovative, you might want to give Viima a try. Our simple but powerful innovation platform takes just minutes to learn and is completely free to get started with!


















.jpg)
