A Guide to Open Innovation Platforms: How to Unlock the Power of Collaboration
As the world continues to evolve at an accelerated pace, so does our pursuit of innovation. But the growing complexity of this world makes innovation more challenging. It’s no longer a one-person job (if it ever was).
Yet, the myth of the solitary genius innovator persists in organizations that still believe that they can innovate alone, with no external help. But no organization is an island.
The most groundbreaking ideas emerge from the collective efforts of many minds. It would be egotistical to believe that an organization can single-handedly create breakthrough innovation and that it possesses all the necessary knowledge, skills, and know-how to do it in the long term.
Co-creation and collaboration are more necessary than ever before, and open innovation can bring together different perspectives, knowledge, research, and skill sets. Open innovation platforms can facilitate this.
So, in this article, we’ll examine the essential functions of open innovation and the ways in which various types of open innovation platforms can help drive innovation. We’ll dive deeper into how they work, their challenges and benefits, and we’ll help you assess whether you need an open innovation platform by providing concrete examples and use cases.
Table of contents

Back to Basics: Defining Open Innovation
While the concept of open innovation is widely recognized, its practical and theoretical applications are not always completely understood. This is because the practice of open innovation can differ from the academic definition, and there is often a gap between theory and practice.
So, to know if your organization can benefit from open innovation, it’s important to have a more nuanced understanding of the topic and to fully appreciate its potential and acknowledge both the benefits and the challenges.
In short, open innovation refers to how companies make sense of their vast networks and base of knowledge and leverage them in unique ways by absorbing external ideas, technologies, trends, business models, and new approaches into a company's own business.
How companies make sense of their vast networks and base of knowledge and leverage them in unique ways by absorbing external ideas, technologies, trends, business models, and new approaches into a company's own business.
In practice, open innovation involves a range of activities from something as simple as asking for ideas from customers to complex ecosystems that follow different models of co-creation and knowledge exchange.
The term is used fairly loosely, so if we distance ourselves from the rigors of its definition, open innovation can cover essentially all creative activities where information goes back and forth through organizational borders. From this point of view, its uses are limitless.
Where it all started
To understand why this is the case, let’s go back 20 years, when the term was first introduced by Henry Chesbrough in his book Open Innovation: The New Imperative for Creating and Profiting from Technology.
Chesbrough argued that the traditional closed innovation model, where companies kept their research and development in-house, was outdated and that companies should instead look to external sources for new ideas and opportunities. By adopting open innovation, companies could improve their competitiveness, grow their market share, and enhance their processes.
Closed innovation relies solely on internal expertise to develop new businesses, while open innovation recognizes that external individuals and organizations can also contribute to achieving strategic goals. Sharing knowledge and intellectual property can and should benefit both parties.
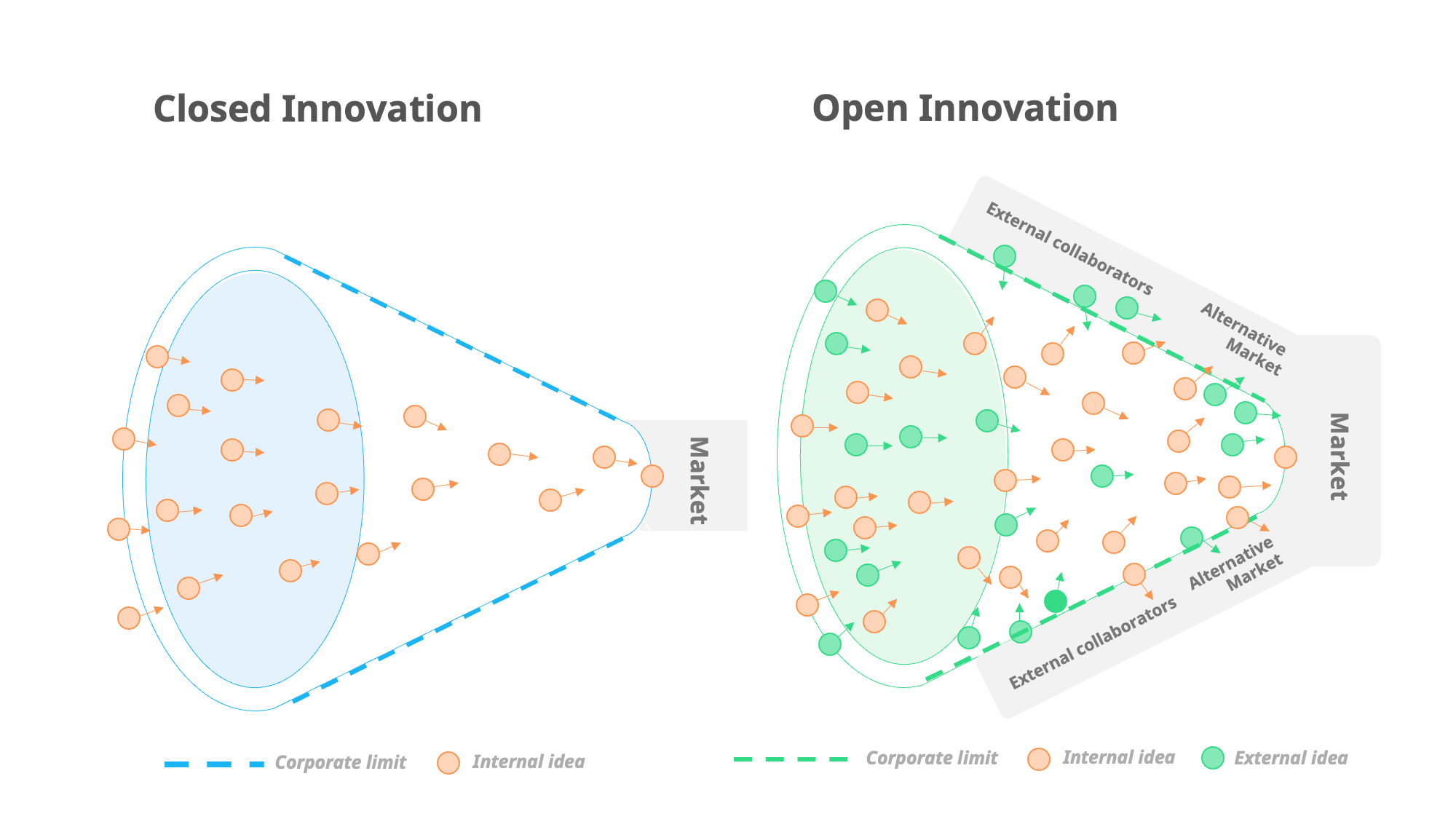
It’s important to note that there is no right or wrong between the two as both closed and open innovation have their place and time. So, it’s not about choosing between A or B, but rather having clarity on when your organization can benefit from both A and B, and how to do it right.
Open innovation is not rocket science, but to make it work you need a systematic approach. This means creating the environment, systems, and processes that allow you to reap the benefits in the long term. To effectively harness the knowledge and creativity of a wide range of individuals you need to start with an open mindset and to understand the tools that can help you facilitate this type of innovation.
We already wrote quite extensively on open innovation and its different types so if you want to dig deeper, check out our other articles on the topic.
Now, let’s get to the meat of this article and see the types of open innovation platforms you can choose from, and how to do it.
The Different Types of Open Innovation
An open innovation platform is a tool meant to support the open innovation process by facilitating collaboration and knowledge-sharing between different organizations or individuals.
An open innovation platform is a tool meant to support the open innovation process by facilitating collaboration and knowledge-sharing between different organizations or individuals.
Just like the different types of open innovation, there are also different platforms. The most important thing is to know head start what you want to achieve with open innovation, what kind of process you want the platform to support, and what features are most important to you.
For this, you should decide beforehand on the open innovation method that best suits your purpose.
Briefly, there are three main approaches to open innovation, as described by Chesbrough:
-
The outside-in (inbound) model involves using external knowledge to support growth in the market. This can include collaborating with other organizations, innovating with the help of suppliers, cooperating with researchers and public entities, or understanding industry trends.
-
In the inside-out (outbound) model you leverage your organization’s capabilities. In this case, the open innovation platforms help you continuously improve on processes, products, or services by tapping into the knowledge of your workforce. Some organizations even use it for intrapreneurship programs or incubators for a more systematic approach.
-
The coupled open innovation model is a mix of the two, combining both inside and outside knowledge to create value.
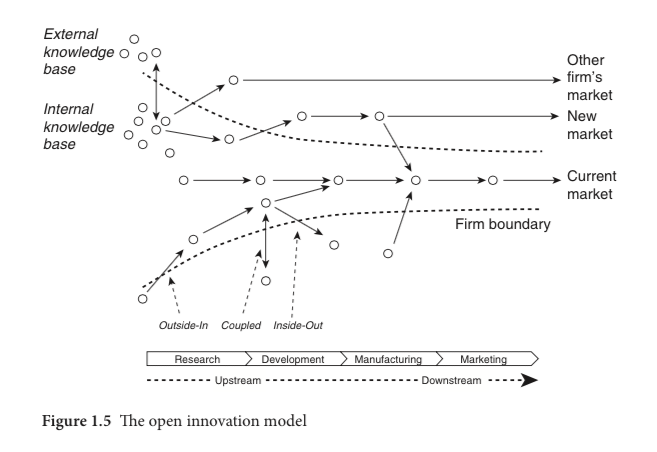
(source: H. Chesbrough, W. Vanhaverbeke and J. West – New Frontiers in Open Innovation, 2014)
Choosing from the Different Types of Open Innovation Platforms
Now that you have a better understanding of how to approach open innovation, you can choose a platform that suits your needs. To help you with this, we’ll next provide a list of possible open innovation platforms. Although it’s not meant as an exhaustive list, we have included platforms that can fulfill most needs effectively.
-
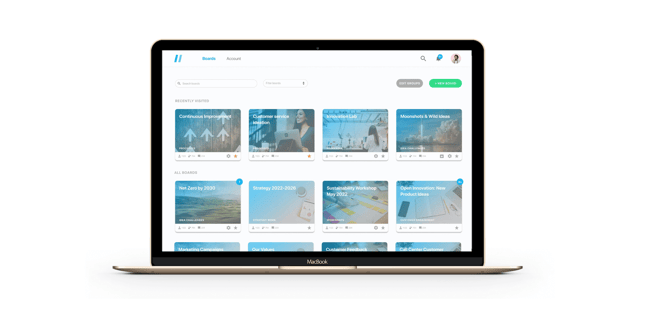
Idea management platforms
These are the most common as they can be used in different ways, not just for open innovation. Such platforms are used to collect, evaluate, and develop ideas from customers or other stakeholders.
These platforms can be highly powerful for the entire open innovation process. There are different types of idea management platforms available, and our two main recommendations are Viima and HYPE Ideation solution, from HYPE Innovation. These are, of course, more than just idea management platforms.
HYPE Ideation, for example, can fit the needs of an idea management platform, but if you want to scale and expand, HYPE Innovation also provides other comprehensive solutions, like trend scouting, technology scouting, partnering, employee engagement and much more.
At the same time, Viima can be used for continuous improvement, strategy collaboration and managing the entire innovation process.
Obviously, the choice between the two comes down to the use case you have, and the type of organization.
Viima
First, both Viima and HYPE Ideation are good options for open innovation as they provide a structured approach for collecting, evaluating, and implementing ideas from external sources such as customers, suppliers, and partners. They make it easier to manage the entire open innovation process, from idea generation to implementation, by providing tools for collaboration, idea ranking, and advanced analytics.
One of the factors that could influence the decision between Viima and HYPE Innovation is who you want to focus on. Viima can fit well in small and medium organizations that don't need any support in setting up the tool and want to take it into use immediately.
But, as you will soon see in our Signify example, it can also be easily scaled for larger organizations that use it with hundreds of suppliers.
HYPE provides additional support and consulting to implement large projects and complex processes that involve thousands of people.
HYPE Ideation
When deciding between Viima and HYPE Innovation, it's important to consider the use case of the open innovation model you choose, the complexity of the innovation process, and the specific needs of the innovation team.
Ultimately, both Viima and HYPE Innovation offer great solutions for open innovation and can help you improve your innovation capabilities. Depending on your organization, you will know better what suits your needs in this case.
-
Crowdsourcing platforms
They are similar to idea management platforms in the sense that they can be used to source ideas and knowledge from a diverse group of people. A dedicated crowdsourcing platform helps you tap into the knowledge, technologies, and research that exists outside the organization.
Crowdsourcing platforms are different from idea management platforms in that they focus on tapping into the collective intelligence of a large group of people, often from outside an organization, to solve problems or generate new ideas. These platforms leverage the power of the crowd to gather insights, feedback, and ideas from a diverse group of people, often at scale.
The main difference between crowdsourcing platforms and idea management platforms is the focus on external participation and the scope of participation.
Some examples of crowdsourcing platforms are:
-
Amazon Mechanical Turk (MTurk)is a popular crowdsourcing platform operated under Amazon Web Services.
It allows businesses and researchers to outsource tasks to a distributed workforce of individuals. The uses of the platform range from building, managing, and evaluating Machine Learning workflows to business process outsourcing. The platform offers a low-cost, scalable solution for businesses that need access to large amounts of human intelligence.
-
InnoCentive (part of Wazoku) is a crowdsourcing platform that connects organizations with a global network of problem solvers.
The platform allows organizations to post innovation challenges and reward individuals or teams that can come up with the best solution. The platform is used by a wide range of industries, including healthcare, energy, and technology, and provides a way for organizations to tap into a global network of experts to solve complex problems.
Other platforms, provide highly specific solutions, like Cad Crowd and Utest.
-
With Cad Crowd you can find professional CAD designers and 3D modelers with proven expertise and knowledge, or to post a design contest and review submissions from multiple participants.
-
Utest, on the other hand, brings together freelance software testers who help some of the most iconic brands to ensure high-quality software for their customers.
-
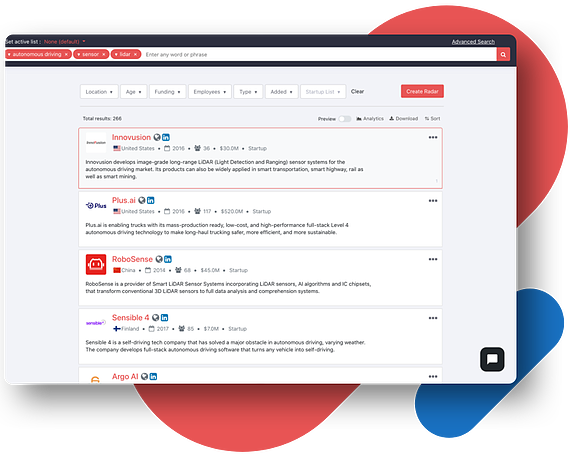
Scouting platforms
Scouting platforms act like innovation marketplaces to help you connect with other organizations and third parties that can provide the technology, services, or expertise that you are missing.
These platforms enable corporate partnerships with start-ups or other entities in a way that is beneficial for both parties. They can also be used to scout for new talent or technologies as well as patents or research papers, to help you overcome specific challenges or provide more in-depth access to information or scientific research.
In the context of open innovation, patent filing can be used to protect and monetize intellectual property, as well as to share it with others through licensing agreements or other forms of collaboration.
By using dedicated platforms, innovators can identify potential areas of overlap or opportunities for collaboration and can better navigate the complex landscape of intellectual property rights.
There are different scouting platforms that can help with patent filling, ranging from free resources like Google Patents and the USPTO database, to paid services like PatSeer and Derwent Innovation and their Derwent World Patent Index.
Derwent Data Analyzer is a useful tool for patent and IP professionals who need to quickly and effectively analyze large sets of patent data to gain insights into the competitive landscape and identify opportunities for innovation.
When it comes to scouting for new talent, technologies or start-ups, HYPE Innovation provides a great solution through HYPE Partnering.
It offers a comprehensive solution for technology scouting, evaluation, and collaboration. You can use it to identify new technology opportunities, evaluate potential partners, and manage partnerships more effectively, ultimately driving innovation and growth.
-
Open data platforms
This is essential in getting a sense of future opportunities or risks so you can better adapt to the upcoming change.
An open data platform can act as a data science environment which helps you identify relevant data and analyze it to gain valuable insights.
There are many open data platforms available that can facilitate open innovation and trend scouting. To name just a few:
-
Google Trends: allows users to track the popularity of search terms over time. This can be a useful tool for identifying emerging trends and understanding consumer behavior.
-
Open Data Institute: a non-profit organization that promotes the use of open data to drive innovation and economic growth. The institute provides a range of tools and resources for working with open data, including training courses and access to datasets.
-
World Bank Data: provides a wide range of data on global development, including economic indicators, demographic data, and environmental data. The data is available in a variety of formats and can be downloaded for free.
-
European Data Portal: provides access to open data from across the European Union. The portal contains data on a wide range of topics, including health, transport, and the environment.
-
GitHub: even though it's meant for collaborative software development, it also hosts a large number of open data repositories. These repositories contain data on a wide range of topics, from climate change to social media trends.
-
Kaggle: a platform for data scientists and machine learning engineers to collaborate on data analysis and modeling competitions. The platform provides a wide range of datasets, as well as tools and resources for exploring and visualizing data.
There is a massive amount of data out there and as time goes by, more and more will be available. You can find here a more extensive list of additional open data sources grouped by regions.
As you can see, access to data is not an issue, but rather how to process all the available information and make sense of it. That’s why, unless you have your dedicated team of data scientists, you might want to use a platform that can analyze and sift through all this information, based on your industry and interests.
The above-mentioned Clarviate, through its Derwent Dana Analyzer service, can help you make sense of all the information out there. Also PatSeer is a great solution to help you connect the dots by bringing together and analyzing data from scientific literature, IP, legal and more.
Obviously, there are different platforms that can serve a variety of purposes. These are just a few that we believe can help you get started with any type of open innovation. In the end, it’s just about your objectives and what you wish to achieve.
Next, we will see why and how open innovation platforms have the power to transform the way you innovate and compete in your market.
The Benefits and Importance of Open Innovation Platforms
The benefits of open innovation platforms and their role are closely linked to how open innovation is put in practice.
Engage larger audiences.
Open innovation platforms increase the audience size potential. To get a maximum input, and better understand consumer behavior, you can expand the audience without any apparent limits. The right platforms give you the flexibility to expand and scale as you grow your open innovation activities, so it’s easy to get input from 1000 people, but also from 100 000 people when the time comes.
Lego's Ideas Site is an example of how companies can engage with consumers and fans all over the world to share their ideas for new products, gaining a better understanding of customer needs and new exciting ideas.
Engage relevant audiences.
In a closed innovation system, the knowledge and skills available to address a particular problem or challenge are limited to the internal resources of the company, i.e., its employees.
.jpg?width=2000&height=1328&name=open%20innovation%20benefits%20large%20audience%20(1).jpg)
On the other hand, open innovation enables you to reach out to external stakeholders, such as customers, suppliers, partners, or even the general public.
Open innovation platforms can be designed to attract specific types of contributors, such as experts in a particular field or individuals with a specific skill set. This targeted approach ensures that the most relevant audiences are engaged in the innovation process.
For example, Signify has a collaborative program called SEED designed to generate ideas for their existing products by leveraging the knowledge of their suppliers. The SEED program is exclusive and collaborative, and only the best suppliers are invited to participate. They use various Viima boards to collect thousands of ideas from hundreds of suppliers, leading to the implementation of more innovative products. We will dive a bit deeper into this example later in this article.
Increased pace of innovation.
Open innovation platforms provide access to a wide pool of ideas and diverse knowledge for more educated decisions. With the right tool, one can build innovation processes with an agile and iterative approach that allows for fast idea testing and validation.
In the closed innovation model, everything is done in-house, and this tends to lead to a lack of openness to discuss ideas and experiment. When organizations open to “the outside world” they get exposed to new perspectives and approaches, leading to solutions they might not have considered otherwise.
For example, Procter & Gamble (P&G) established the Connect + Develop program, an open innovation initiative that seeks to find and acquire external technologies, products, and ideas to supplement their internal R&D efforts. One of their many success stories is how their collaboration with EPAM Continuum resulted in the creation of the Swiffer cleaning product, which generated billions of dollars in revenue for the company.
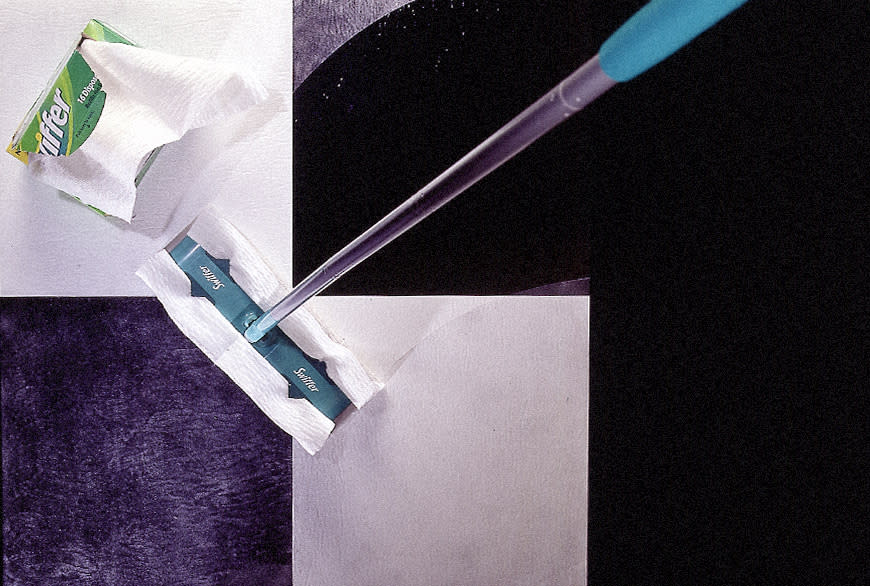
P&G has managed over the years to successfully communicate their needs to a global network of innovators who can help them accelerate their pace of innovation.
Cost efficiency
Innovation costs are greater than ever before and according to studies, while R&D investments are much higher than they used to be 90 years ago, the output is not significantly better.
On the other hand, the overall costs of open innovation are usually smaller in relation to the number of ideas and input. Open innovation platforms can reduce R&D costs and provide access to cost-effective solutions. Instead of relying solely on acquisitions of startups and their technologies, organizations can drive their own innovation and empower their teams.
For example, Eli Lily, a pharmaceutical company used open innovation to reduce costs by collaborating with external researchers and scientists to find new drug candidates. By tapping into the expertise of external collaborators, Eli Lilly was able to reduce R&D internal costs, while also expanding the potential pool of ideas and innovations.
Through external collaboration, they got novel perspectives and innovative solutions that the company may not have considered otherwise.
Win buy-in and reduce risk.
During difficult times, companies typically reduce their R&D budgets and cancel innovation projects. It becomes challenging to justify higher risk and investments that may or may not yield long-term benefits when the immediate future appears uncertain.
Some organizations use open innovation platforms to scout for data and access a global network of problem solvers that can help mitigate risk and find solutions that can demonstrate their potential value.
Open innovation platforms can transform the way companies innovate and stay competitive by accessing new ideas, resources, and expertise. However, they also come with a set of challenges that need to be addressed. So, let’s explore these challenges and possible solutions.
Implementing Open Innovation Platforms: Challenges and Success Factors
The logic and business reasons for open innovation are well-understood, yet executing it is still a struggle for many organizations facing a range of challenges that can impede success. To fully benefit from open innovation, it is essential to understand and address these challenges.
The main challenges and obstacles in implementing open innovation platforms can be grouped into four categories: strategic, operational, legal, and cultural.
-
Strategic challenges
Strategic challenges are mostly related to the goals and objectives of the open innovation platform. People might often ask themselves: “do we really need it and is it complementing the organization's overall strategy in any way?
That’s why it’s essential to clearly define the goals and communicate them. What do you want to achieve through the use of the open innovation platform, what problems do you expect to solve, and how do you align with the strategic goals of the organizations?
It's important to keep in mind that there may be trial and error involved, despite any research or planning. Piloting open innovation platforms can help test the platform's compatibility, as well as identify any issues with current processes or goals. Some vendors, like Viima, offer free versions or demos, which can be helpful when deciding on a platform.
-
Operational challenges
Operational challenges span from concerns about integration with existing processes and systems, day-to-day management, and execution of the platform to maintaining the quality and commitment of collaborations.
To overcome this, you need to build an effective process around your open innovation platform. It’s also important to have a flexible tool that can fit your specific use cases and needs and can be easily integrated into your current systems. However, pay attention to vendors that oversell because there is no one-size-fits-all solution to cover everything on the topic.
To maintain commitment, but also the quality and relevance of contribution, enhance and reward engagement. The rewards that are most effective in keeping people engaged are usually intrinsic, like a sense of acknowledgment, accountability, and responsibility for one's actions and contributions.
By recognizing the value and impact of one's work and taking ownership of it, individuals are more likely to stay motivated and engaged in their tasks.
A good open innovation platform provides a transparent environment for this. Extrinsic motivators like bonuses or other material rewards could also work, but only in the short term for that extra push. in the long term, material rewards won’t deliver the best results as people could be participating just for the sake of rewards and come up with suboptimal ideas.
-
Legal challenges
Legal challenges are some of the most brought up by organizations. These can refer to intellectual property (IP) issues, confidentiality concerns, and compliance with regulations.
These are all valid concerns as it is normal for organizations to be protective of their confidential information and intellectual property, and in some open innovation situations, things can get complex. But keep in mind that sometimes these fears do get blown completely out of proportion, even in extremely simple and straightforward situations.
With open innovation initiatives, it is recommended to seek advice from a reputable legal professional. We can’t advise you on legal matters, but to mitigate IP-related risks in the open innovation process, the simplest strategy is to get the rights to all IP generated by participants during the collaboration process.
This can decrease the risk of disputes and provides a clear framework for the use and dissemination of ideas generated by the collaborative effort. In some cases, it may be best to use a non-disclosure agreement (NDA) to further protect sensitive information and trade secrets.
Ultimately, a well-executed IP strategy is critical to successful open innovation. By carefully managing IP, and working with legal professionals when needed, you can maximize the benefits of open innovation while minimizing legal risks and potential pitfalls.
Some idea management platforms, like Viima, have built-in terms and conditions that can be customized to allow whatever legal requirements you may have, such as transferring the rights of submitted ideas if not agreed otherwise.
-
Cultural challenges
Cultural challenges come down to psychological barriers. The different mindsets and attitudes, when faced with change and uncertainty, can lead to a lack of trust and difficult collaboration between stakeholders. These attitudes can come from personal insecurities or from miscommunication.
This is, of course, a vast topic that goes back to the culture of your organization and whether it has been cultivated to encourage innovation and continuous improvement.
To overcome this, make sure you communicate very well the process, goals, and role of all those involved and set examples of how an open innovation platform can benefit them. Offer training and show proof of the benefits of co-creation and collaboration within that platform. Be sure you’re on the same page and that you have a common understanding of the expectations, terms, and concepts.
Examples of Successful Use Open Innovation Platforms
Now, let's see some examples of companies that have effectively leveraged open innovation platforms to achieve their business objectives.
As mentioned, co-creation is a form of open innovation and companies can work with different stakeholders to develop new products, services, or solutions. Signify leveraged the knowledge of its suppliers through its SEED program to drive innovation and create value for its customers.
For this, they used Viima as their go-to open innovation and collaboration platform. It enabled them to access a wider range of ideas and expertise by bringing together selected suppliers. Using a dedicated platform allowed them to have control over the development process by only inviting the best suppliers that meet their high standards for quality and performance.

Signify's SEED program
Through this process Signify can bring new, innovative solutions to the market more quickly and efficiently, while also creating value for its customers.
In short, by using an open innovation platform, Signify managed to:
-
Access a wider range of ideas and expertise: Viima enabled Signify to tap into a wider range of ideas and expertise than would have been possible through its internal R&D efforts alone.
-
Accelerate innovation: By collaborating with external partners, Signify was able to accelerate its innovation efforts and bring new products and solutions to market.
-
Enhance customer value: Using an open innovation platform enabled Signify to better understand and meet the needs of its customers by bringing in new perspectives and ideas from external partners.
-
Improve collaboration and culture: Viima fostered a culture of innovation and collaboration for Signify as suppliers were satisfied with the new method through which they were able to collaborate.
-
Liebherr
Liebherr is one of the world's largest manufacturers of construction machinery with 11 different divisions, one of which is the domestic appliances one. Liebherr was no stranger to innovation campaign, and this time, with help from HYPE Innovation, they wanted to turn to their customers for innovative solutions.
The project, called “Wine Experience” focused on identifying significant pain points associated with wine consumption and storage while using wine cabinets.
The project had four main phases:
- Creating and engaging an online market research community,
- Developing internal idea campaigns,
- Launching a crowdsourcing campaign with customers, and
- Evaluating the results.
The Innovation Team oversaw interactions on the open innovation platform and ensured they involved the right people at the right time.
The campaign resulted in 139 product and digital service ideas, as well as 639 comments. The project received nearly 10,000 page-views, resulting in 2,300 user sessions.
Using an open innovation tool was crucial in this process, providing the necessary platform to launch the crowdsourcing campaign, as well as tight coordination among different functions, ensuring the success of the project.
For more examples of successful uses of open innovation platforms, you can go to HYPE and Viima's dedicated pages.
Conclusions
Open innovation platforms are powerful tools that can help organizations tap into the collective knowledge and expertise of a wider network of stakeholders to drive innovation. By enabling collaboration, communication, and ideation across different departments, industries, and geographies, these platforms can help organizations unlock new opportunities and stay ahead of the competition.
If you consider open innovation or you’re already doing it but find it difficult to decide on the right platform, remember to first and foremost carefully evaluate your innovation needs and goals.
You should also be prepared to invest in the necessary resources and capabilities to ensure that once you choose a platform it’s used effectively, and that the insights and ideas generated are acted upon in a timely and efficient manner.
Last, but not least, open innovation is not a one-time thing. Just like it’s the case with other types of innovation, you need a continuous process of engagement, and collaboration.
We recommend starting small and testing your open innovation process through experimentation.
If you're looking for a user-friendly, intuitive and efficient platform to manage your open innovation initiatives, check out our Open Innovation Board, customised for this purpose. Sign up for free and start collecting, and developing the most promising ideas!